BRCA Clinical and Protein Data
تفاصيل العمل
BRCA Clinical and Protein Data
Description
This dataset contains clinical and protein expression data for patients diagnosed with BRCA (Breast Cancer). The dataset combines various clinical attributes, including patient demographics, tumor characteristics, hormone receptor status, and surgical details, with protein expression data. It is intended for research purposes, particularly for analyzing the relationships between clinical features and molecular data to understand disease progression and treatment outcomes.
Data Overview
The dataset consists of the following columns:
Patient_ID: Unique identifier assigned to each patient.
Age: Patient's age at the time of diagnosis.
Gender: Patient's gender (e.g., FEMALE).
Protein1, Protein2, Protein3, Protein4: Measured levels of various proteins related to the patient’s condition. These proteins may be biomarkers that help in understanding the biological processes of the cancer.
Tumour_Stage: The clinical stage of the tumor, which provides insight into how advanced the cancer is (e.g., Stage I, II, III). This is based on criteria such as tumor size and the spread of the disease.
Histology: The type of tissue abnormality (e.g., Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma, Mucinous Carcinoma), which helps in classifying the nature of the breast cancer.
ER status (Estrogen Receptor): Whether the cancer cells have estrogen receptors (Positive or Negative). This status is crucial for determining whether hormone therapy is suitable.
PR status (Progesterone Receptor): Whether the cancer cells have progesterone receptors (Positive or Negative). Like ER status, this helps guide treatment decisions.
HER2 status: The status of HER2 protein receptors, which can be either Positive or Negative. HER2-positive breast cancers tend to grow more aggressively, and specific therapies target this receptor.
Surgery_type: The type of surgery the patient underwent (e.g., Lumpectomy, Modified Radical Mastectomy). This indicates the surgical approach taken to remove the tumor.
Date_of_Surgery: The exact date when the surgical procedure was performed.
Date_of_Last_Visit: The date of the patient's most recent follow-up visit, which is used to track the patient's post-surgery progress and overall health.
Patient_Status: The current health status of the patient (Alive or Dead) at the time of the last visit. This helps in analyzing survival outcomes.
Tumor_Stage_Numeric: A numerical representation of the tumor stage (e.g., 1, 2, 3), used for more granular analysis.
Year_of_Surgery: The year in which the surgery was performed, which can help in time-based analysis, especially for longitudinal studies.
EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis)
The following insights have been drawn from the analysis of the BRCA dataset:
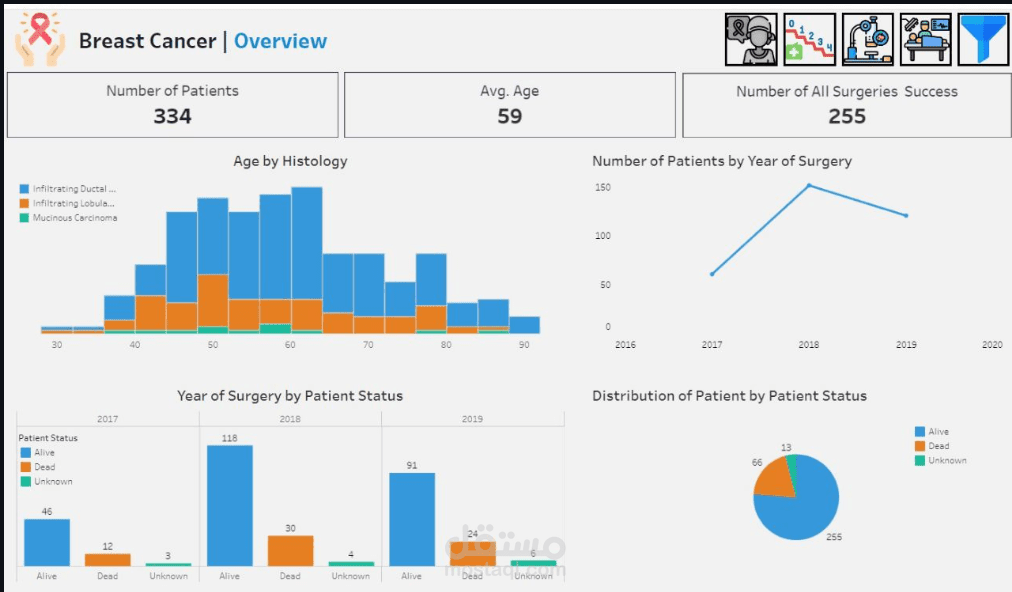
Patient Age Distribution: The majority of patients diagnosed with cancer fall within the age range of 35 to 89 years. This wide range emphasizes the need for early screening across various age groups.
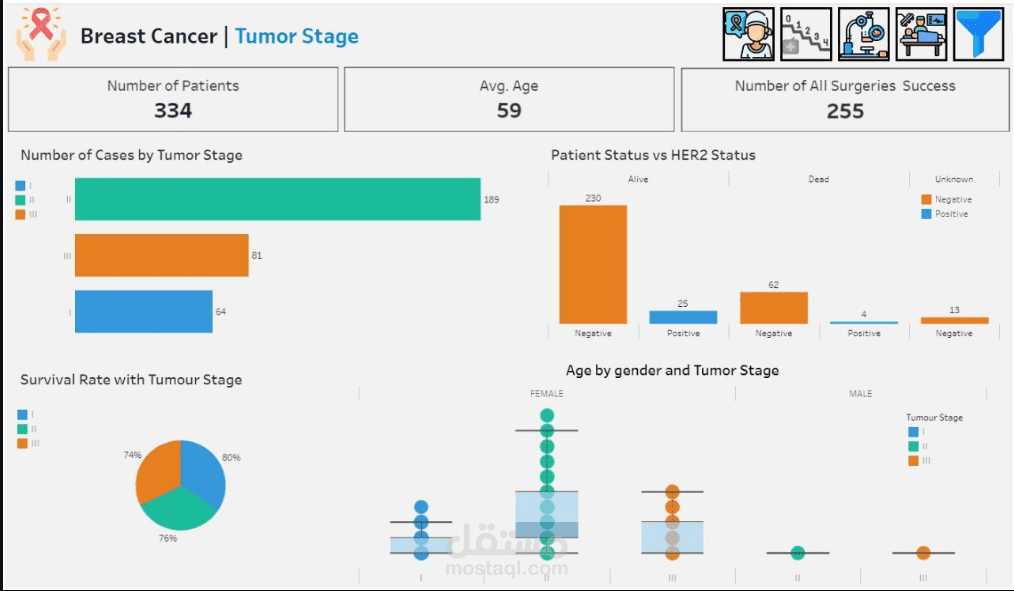
Cancer Stage Awareness: Most patients discover the disease at Stage II, highlighting the critical need for earlier detection and education.
Surgery Trends: The highest number of surgeries occurred in 2018. Interestingly, most patients who underwent surgery are currently alive, with 2017 seeing the lowest number of surgeries.
Gender Disparity: The majority of patients are women, though the data reveals that a smaller proportion of men are also affected by the disease.
Survival Rates: Approximately 77% of patients survived, while 20% succumbed to the disease. These figures underscore the severe risk posed by breast cancer.
Age Distribution Validation: The histogram confirms the age distribution insights observed earlier, reinforcing the significant age range of affected individuals.
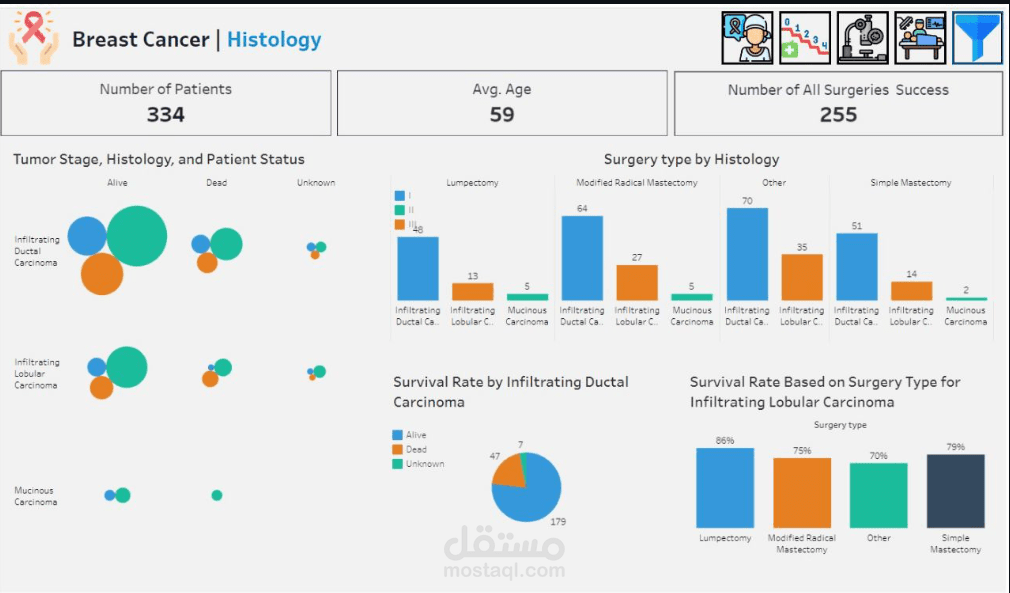
Histology-Specific Insights:
Mucinous Carcinoma: Discovered primarily in Stages I and II. Unfortunately, patients reaching Stage II face higher mortality rates.
Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma: Occurs across all ages but predominantly in Stage I.
Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma: Also seen across all ages, with most cases detected in Stage I.
HER2 Status and Survival:
HER2 Negative: Approximately 79% of patients are alive, while 21% have passed away.
HER2 Positive: Around 87% of patients are alive, with 13% deceased.
Surgical Success Rates:
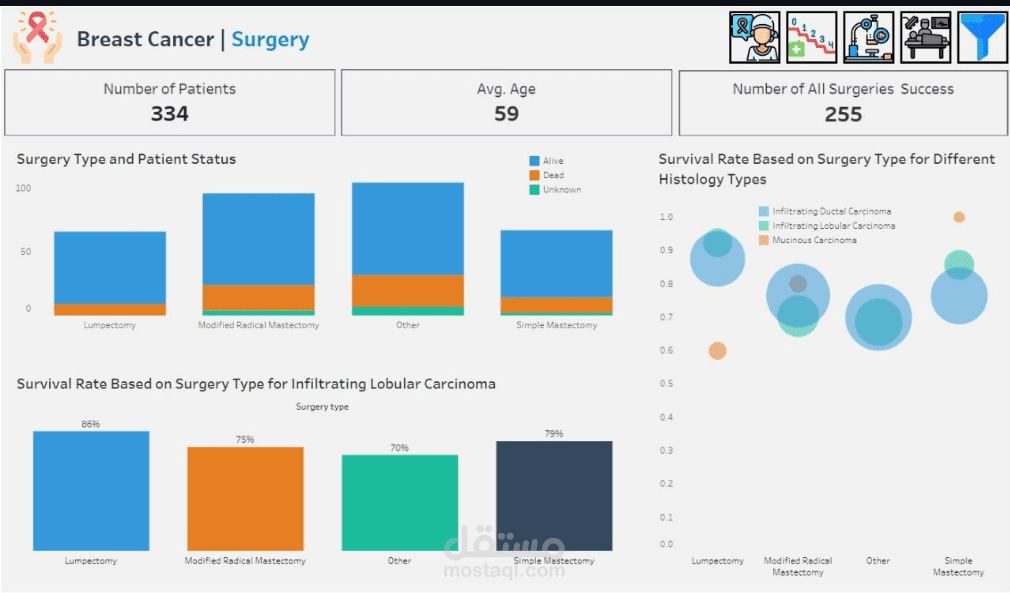
Lumpectomy: The most successful surgery, with 86% survival and 14% mortality.
Modified Radical Mastectomy: Has a slightly lower success rate, with 78% survival and 22% mortality.
Surgery Distribution: As highlighted earlier, 2018 saw the highest number of surgeries, while 2017 experienced the lowest.
Histology and Surgery Correlation:
Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma: Managed through various surgeries, but Lumpectomy and Modified Radical Mastectomy are commonly employed.
Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma: Also treated with different surgeries, though Lumpectomy and Modified Radical Mastectomy remain the most frequent choices.
Protein Correlation Insights
Protein Correlations: Scatter plots with linear patterns between specific protein pairs suggest possible correlations between these proteins.
Histology Patterns: Certain histological types cluster around particular protein combinations, offering insights into how different cancer types may relate to protein expression.
Protein Distributions: The diagonal histograms illustrate the distribution of each protein, revealing patterns like skewness, multimodality, or normal distribution.
These findings provide a deep dive into the clinical and protein expression data, offering valuable insights into breast cancer diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes.
Visualizations and Insights
Data visualization is more than just presenting numbers in a graphical format—it’s the key to unlocking the hidden meanings within complex datasets. By transforming raw data into visual insights, we can bridge the gap between information and understanding. It enables us to quickly identify patterns, spot trends, and make data-driven decisions that are both informed and impactful. Visualization makes the invisible, visible—guiding us from raw information to actionable insights.
1. How does the type of surgery affect long-term patient outcomes?
The most effective surgery for long-term outcomes is Lumpectomy, showing the highest survival rate.
Conversely, Modified Radical Mastectomy is associated with higher risks, indicating it requires specialized medical expertise for better results.
2. Which age group benefits the most from each surgery?
Modified Radical Mastectomy: Most common among patients aged 55-59.
Lumpectomy: Most common among patients aged 60-64.
Simple Mastectomy: Most common among patients aged 50-54.
Other Surgeries: Most common among patients aged 55-59.
3. What is the most common age group among males and females diagnosed with cancer?
Health agencies should consider cancer screening policies targeting women at age 59 and men at age 44, as these are the most common age groups diagnosed with cancer.
4. What is the most common tumor stage at the time of diagnosis?
A higher proportion of early-stage diagnoses suggests effective screening programs.
A significant number of late-stage diagnoses indicate a need for improved early detection efforts.
5. What is the survival rate based on the tumor stage at the time of surgery?
Patients diagnosed at earlier stages have significantly higher survival rates.
This highlights the importance of early detection in improving outcomes after surgery.
6. What is the distribution of surgery types across different tumor stages?
Stage I: Lumpectomy is the most common procedure, indicating a preference for breast-conserving surgery in early-stage cancer.
Stage II: Lumpectomy remains prevalent, but the use of Modified Radical Mastectomy increases.
Stage III: Modified Radical Mastectomy becomes the dominant surgery, reflecting more aggressive interventions in advanced stages.
7. What percentage of patients diagnosed with Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma survived after treatment?
For Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma, when the survival rate is low, more aggressive treatments may be necessary.
High survival rates might justify less invasive treatments to reduce side effects and improve quality of life.
8. What was the most common surgery performed on patients with Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma, and how did it impact survival?
Lumpectomy was the most frequently performed surgery for Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma, showing favorable survival outcomes.
9. What is the best surgery for each histology type?
Lumpectomy: Preferred for both Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) and Infiltrating Lobular Carcinoma (ILC).
Simple Mastectomy: Most effective for Mucinous Carcinoma
Dynamic Dashboard for Advanced Data Analysis and Insight Discovery
This dashboard serves as a powerful tool to explore and visualize complex breast cancer data, turning raw information into actionable insights. It provides a comprehensive view of patient demographics, tumor stages, and treatment outcomes, helping healthcare professionals, analysts, and decision-makers devise data-driven strategies to improve patient care and long-term outcomes. By analyzing key patterns such as surgery success rates, survival statistics, and the impact of different treatment approaches, this dashboard enables the formulation of effective strategies for improving care.