Wind Farms Site Selection Using Geomatics and AHP
تفاصيل العمل
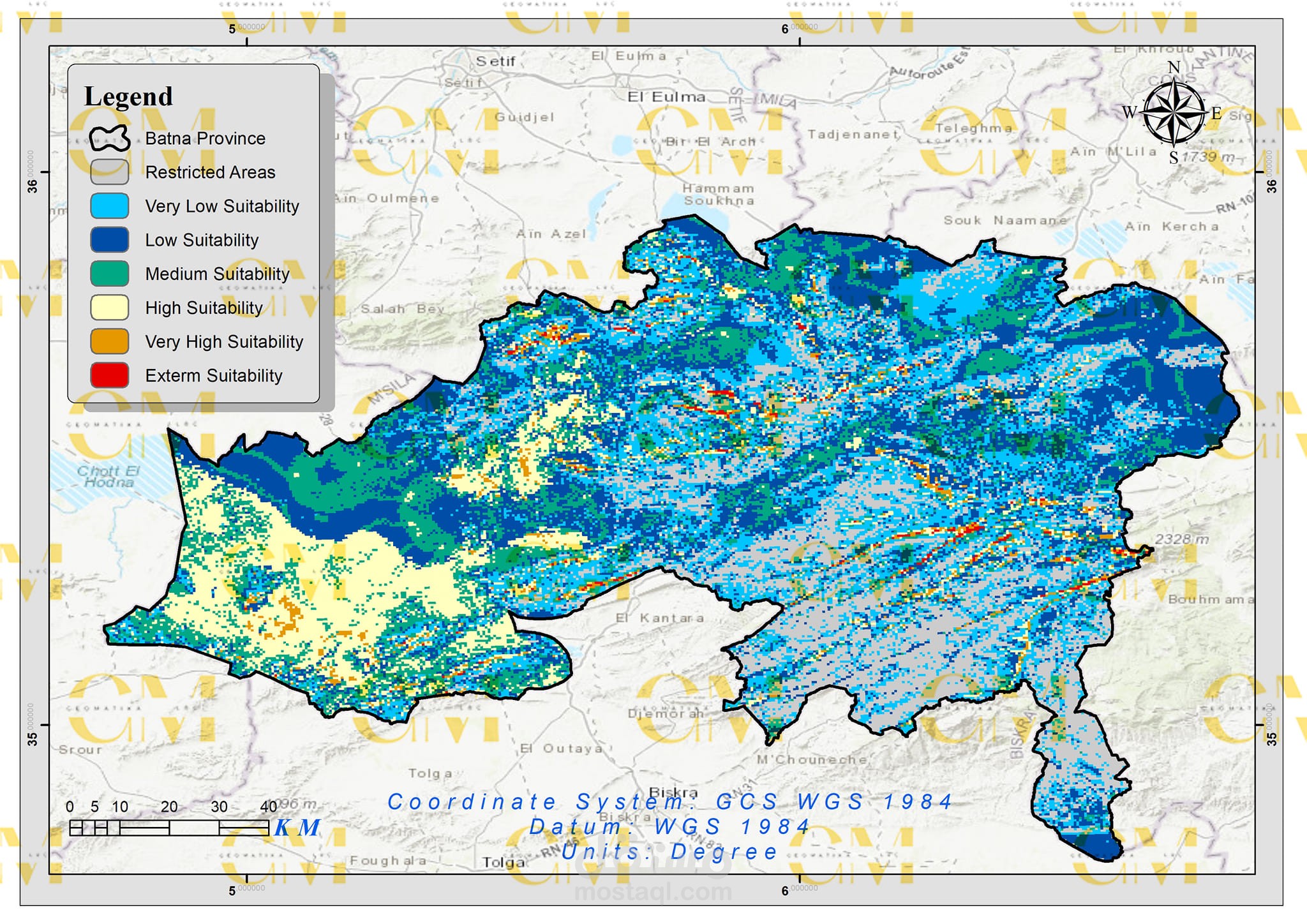
Wind farm site selection is a critical process that requires the integration of geomatics and multi-criteria decision-making techniques, such as Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Geomatics, a field encompassing geographic information systems (GIS) and remote sensing, plays a pivotal role in this process.
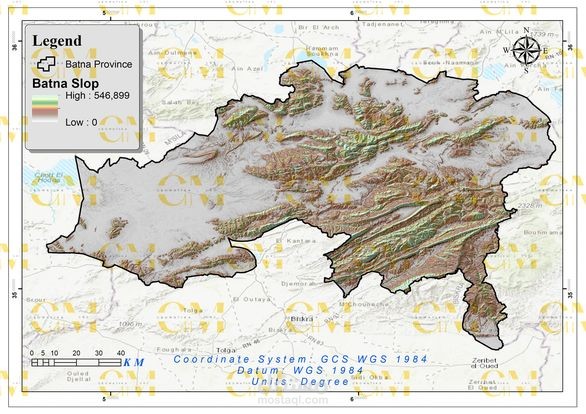
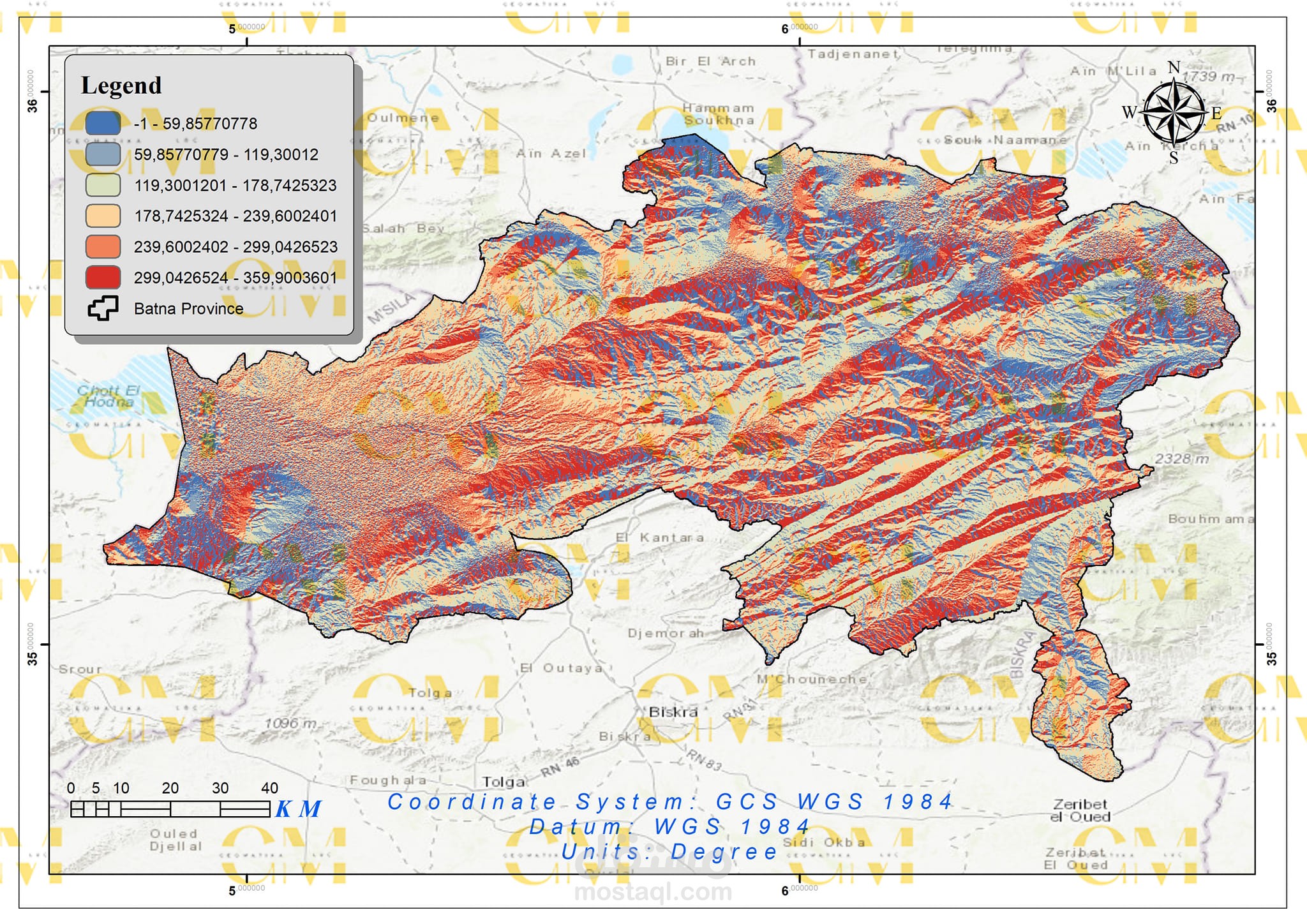
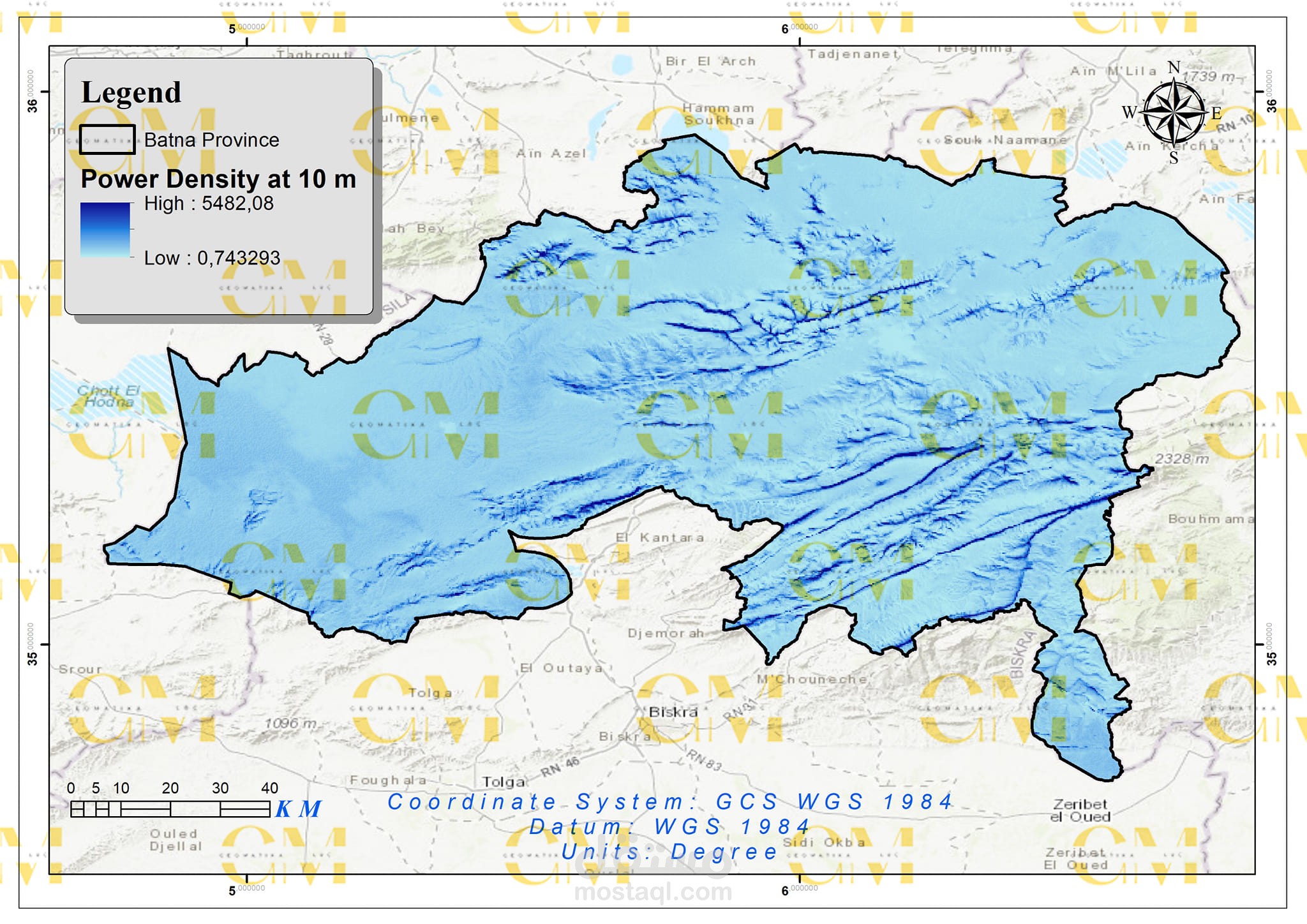
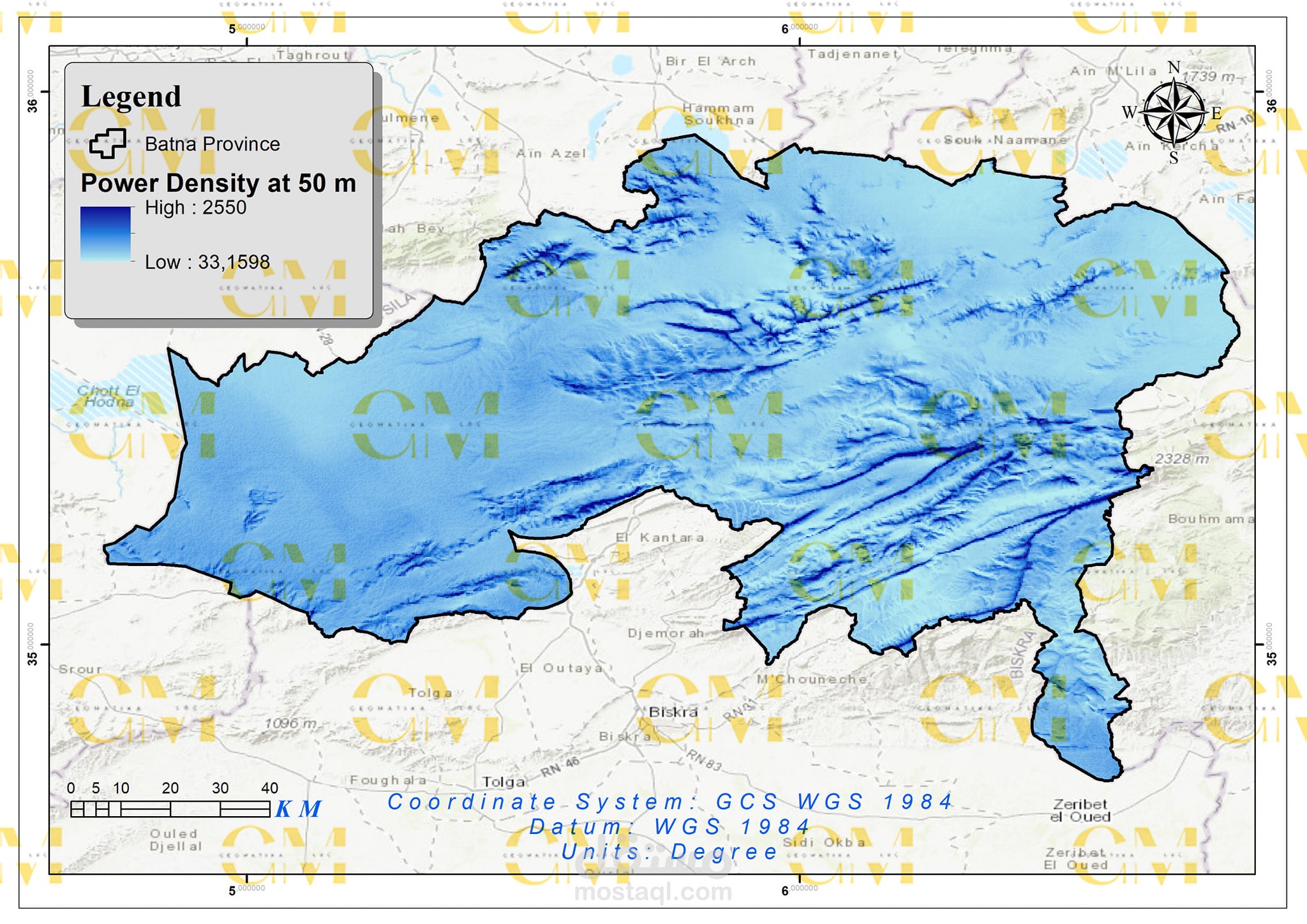
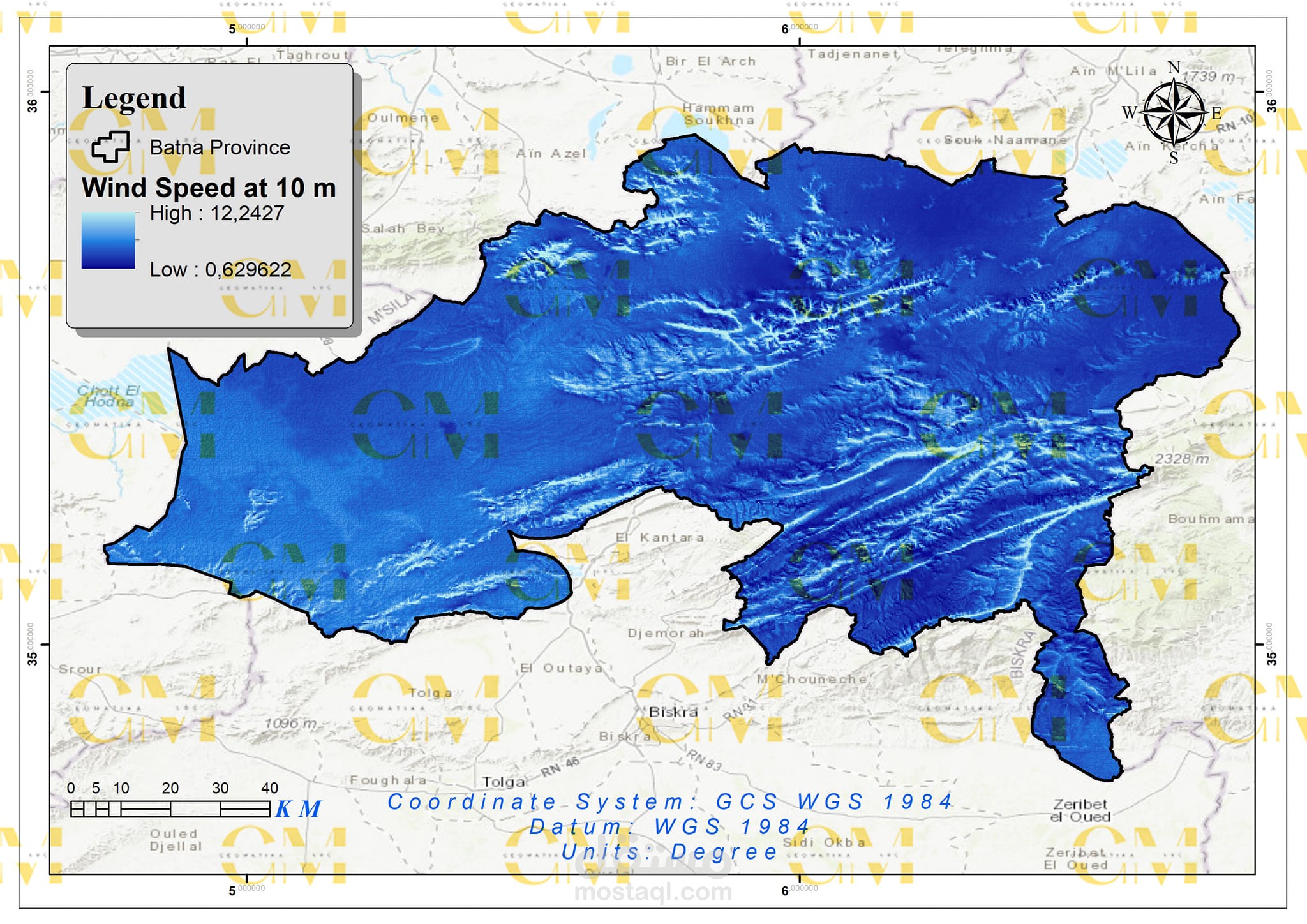
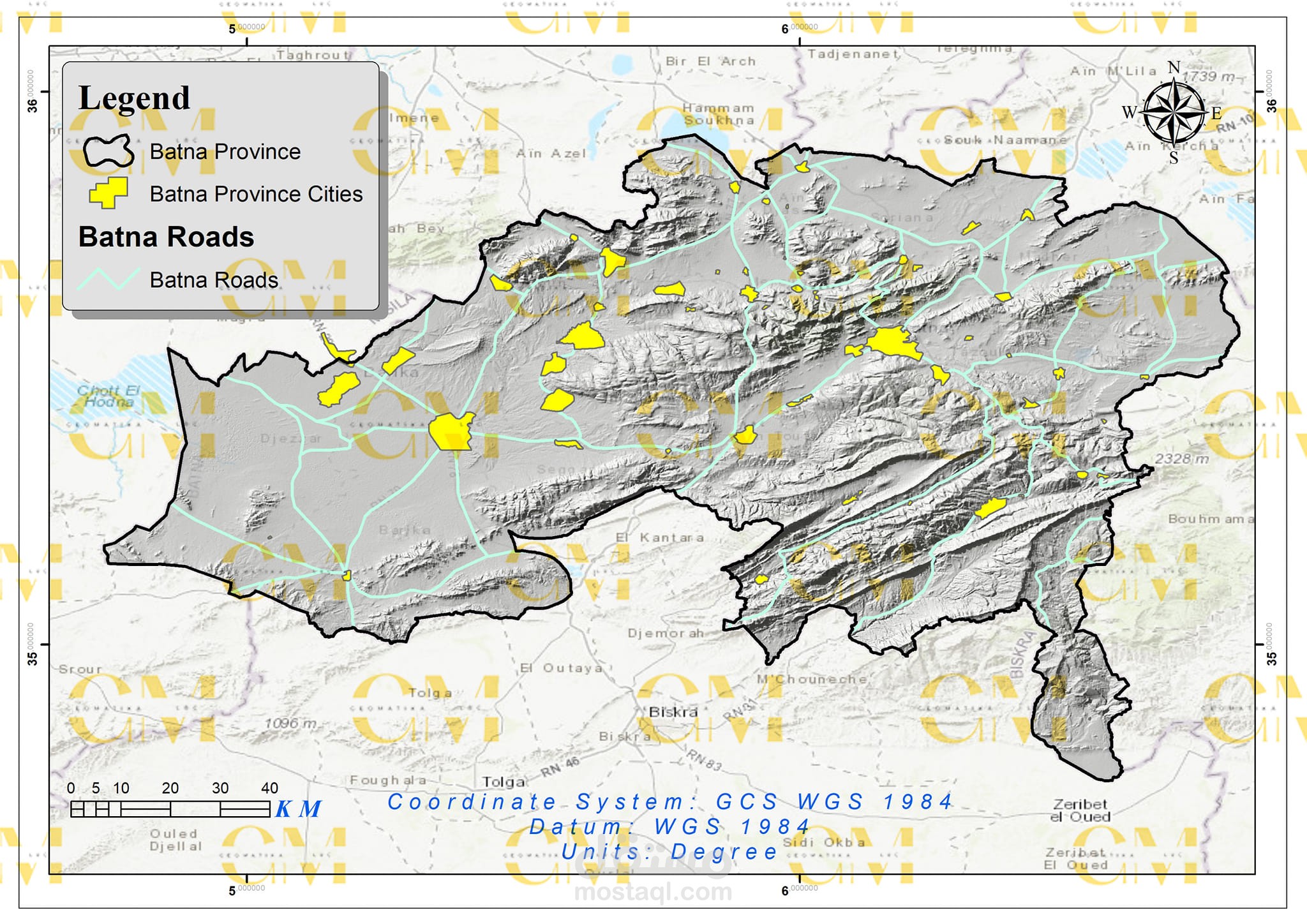
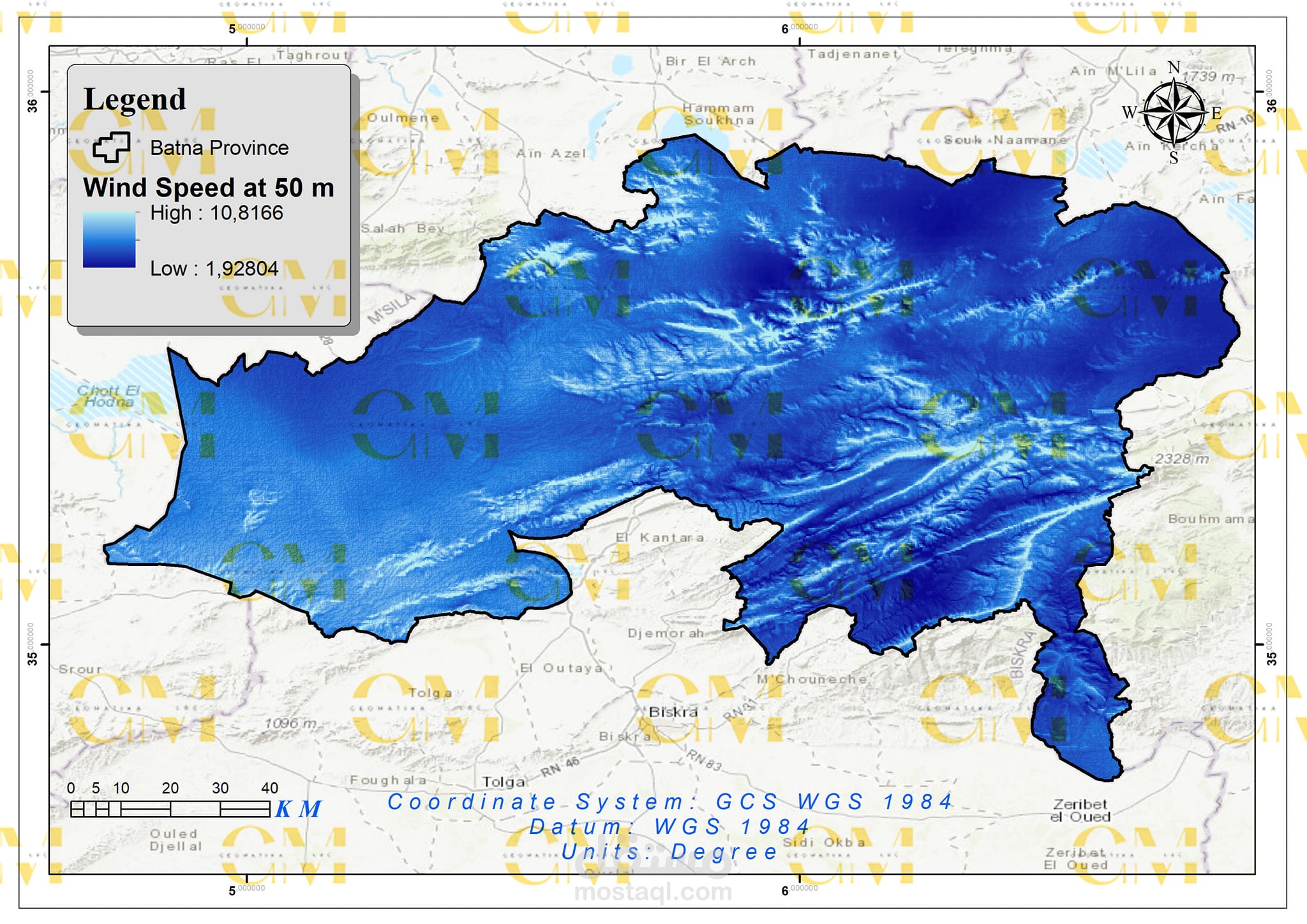
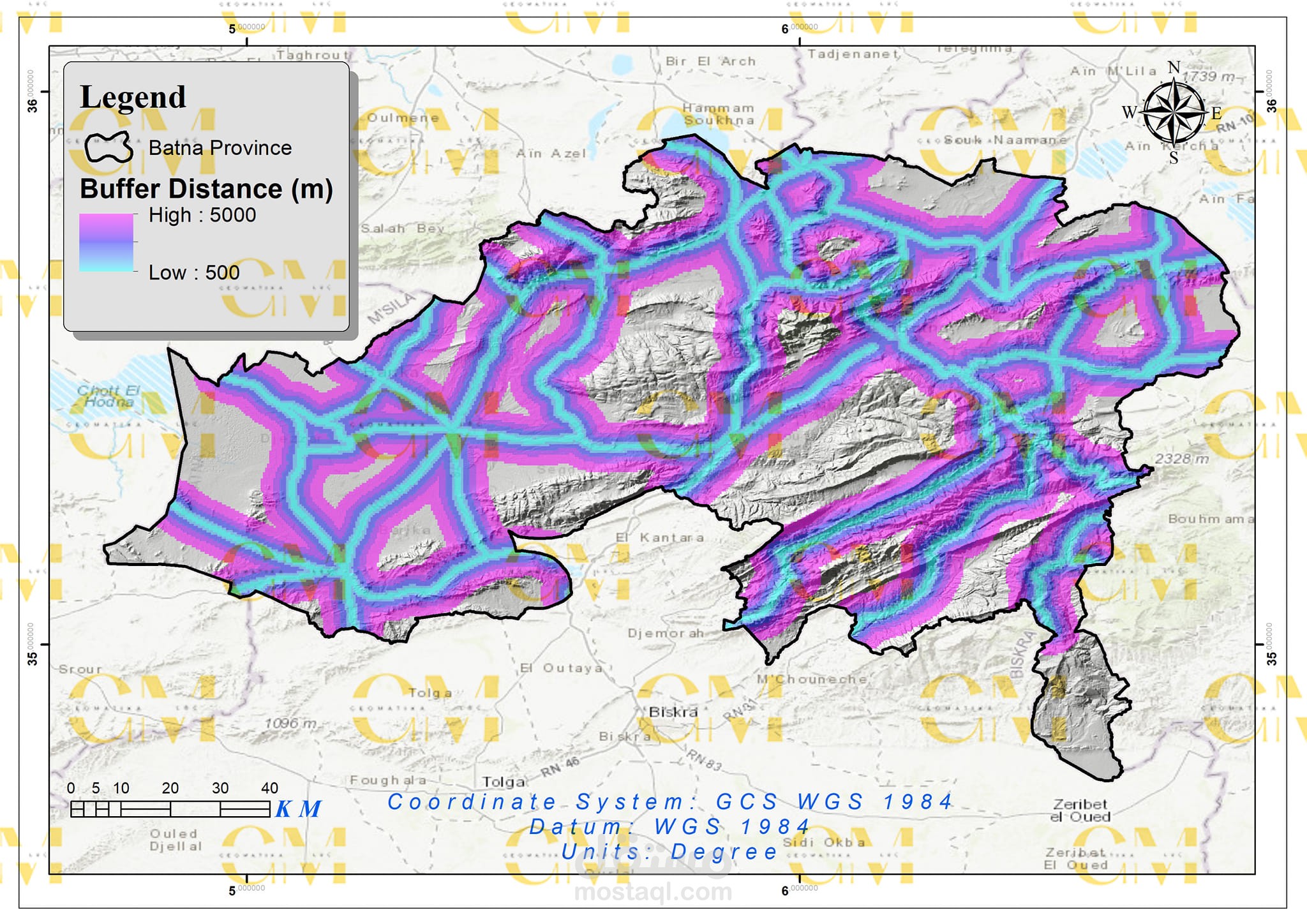
Data Collection: Geomatics engineers utilize GIS to gather spatial data, including wind speed, terrain elevation, land use, and environmental constraints.
Data Analysis: GIS enables the analysis of these datasets to identify suitable areas for wind farms. Factors like wind resource availability, proximity to infrastructure, and environmental impact are considered.
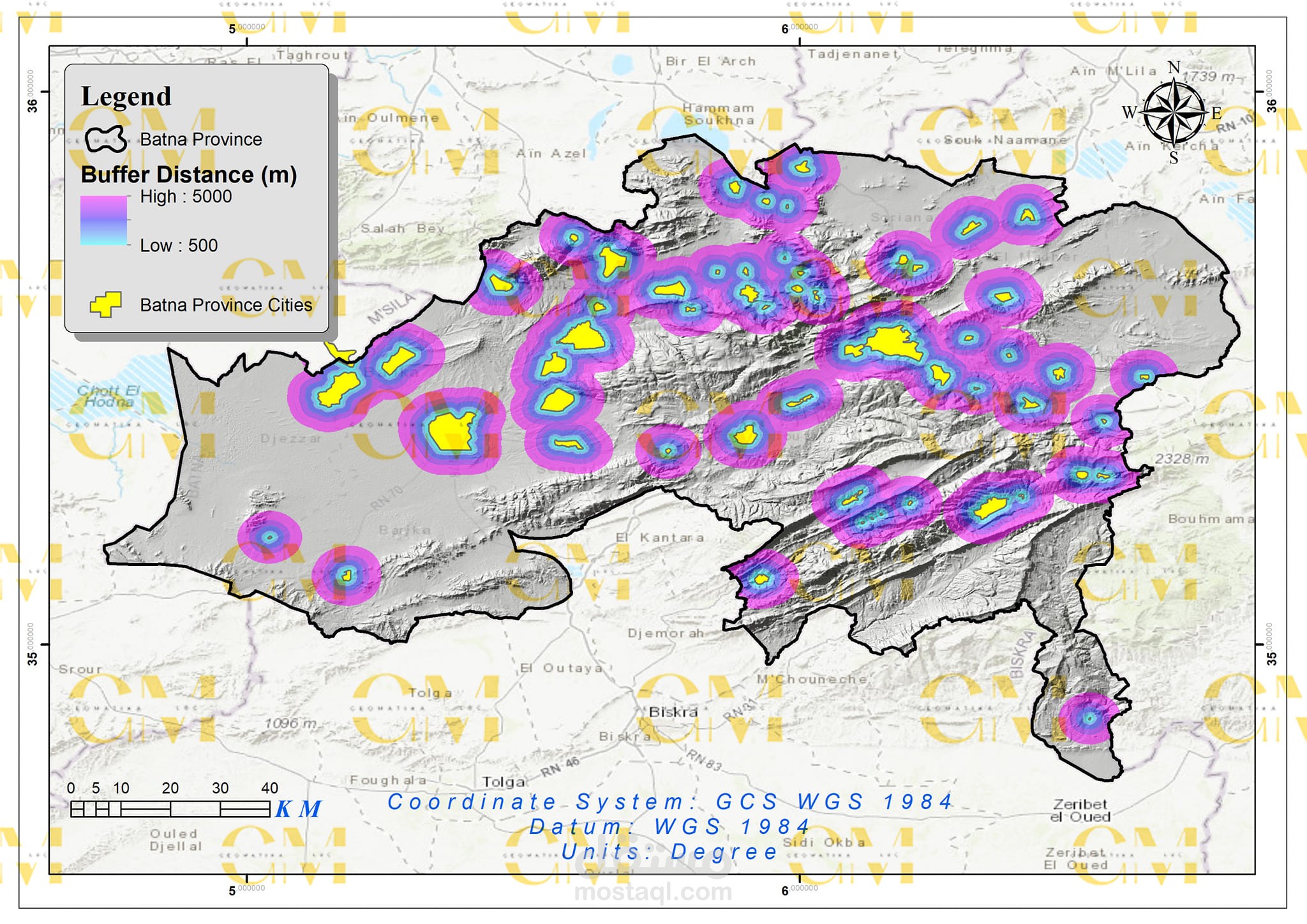
AHP Decision Model: AHP is employed to assign weights to each criterion based on their importance. Geomatics helps in quantifying and visualizing these criteria spatially.
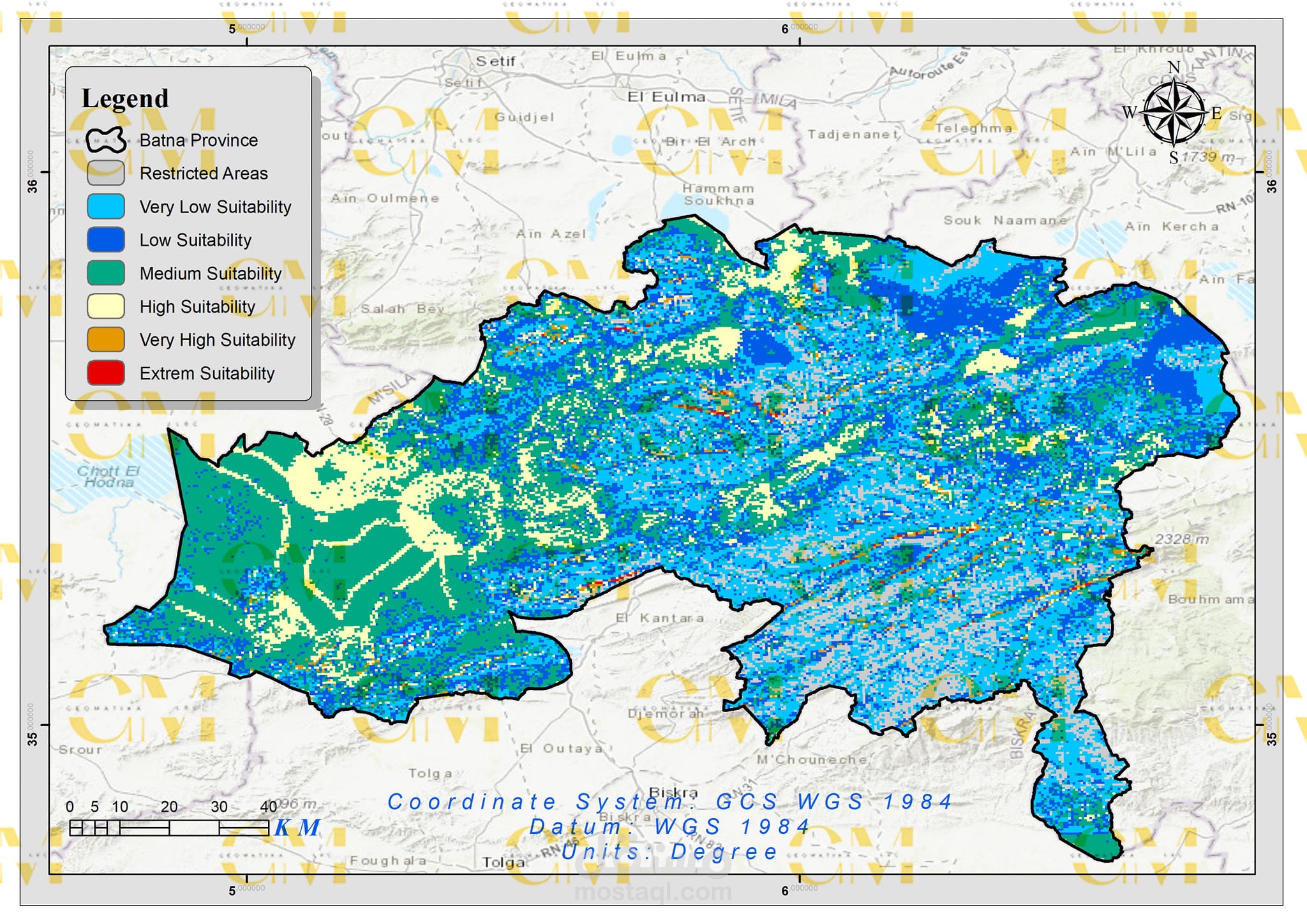
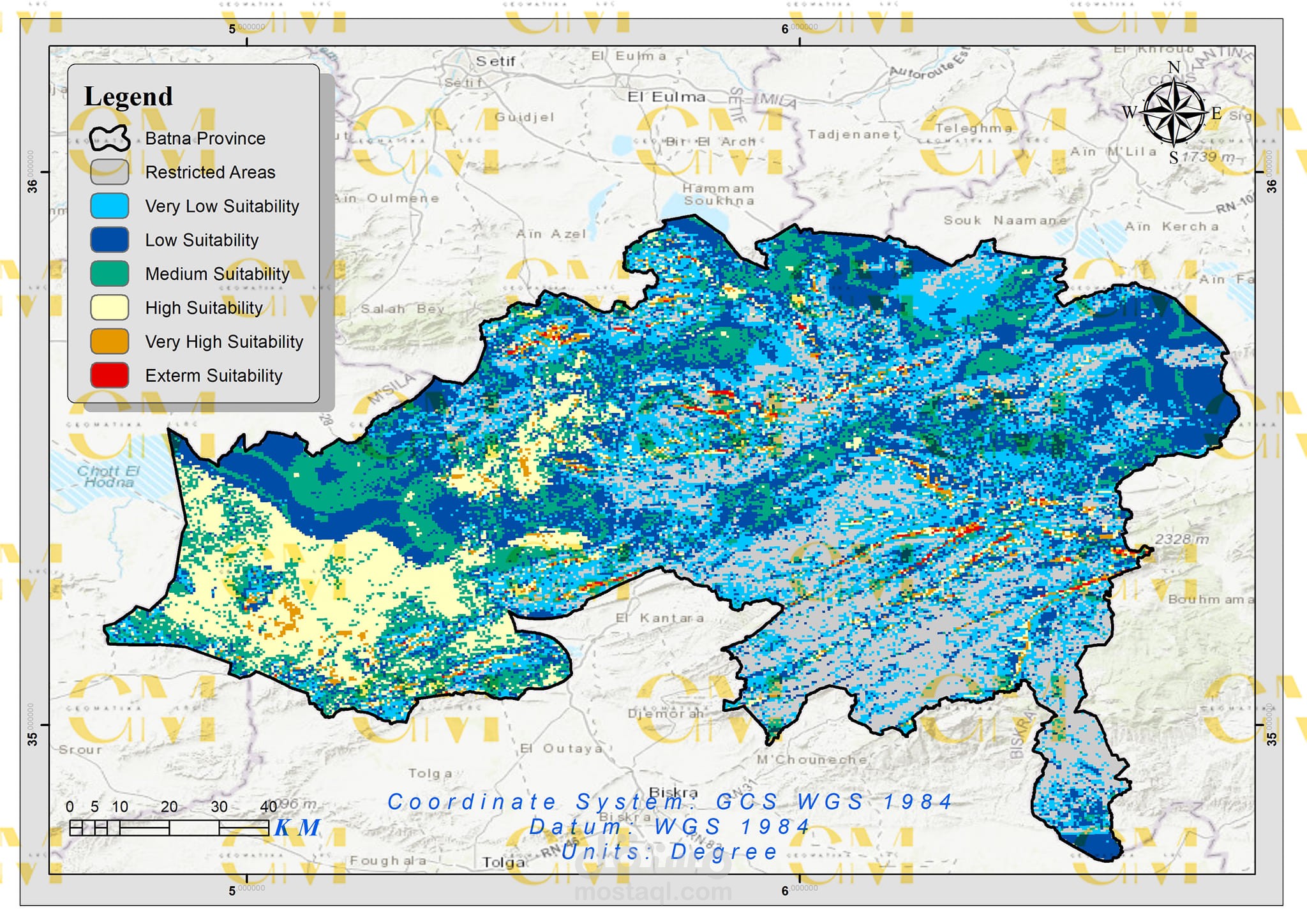
Multi-Criteria Evaluation: GIS and AHP work together to evaluate potential sites by comparing their suitability scores against defined criteria.
Visualization: Geomatics tools allow engineers to create maps and visual representations of potential wind farm sites, aiding in decision-making and stakeholder communication.
Environmental Impact Assessment: Geomatics also facilitates the assessment of environmental impacts, helping ensure sustainable wind farm development.
In summary, geomatics, in combination with AHP, streamlines the complex process of wind farm site selection by providing data-driven decision support and visualization capabilities. This approach ensures that chosen sites are not only economically viable but also environmentally responsible, contributing to the sustainable growth of renewable energy infrastructure.
بطاقة العمل
| اسم المستقل | حليم ر. |
| عدد الإعجابات | 0 |
| عدد المشاهدات | 39 |
| تاريخ الإضافة | |
| تاريخ الإنجاز |