Geomatics for land slids detection in Jijel Province
تفاصيل العمل
As a geomatic engineer, utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing techniques in landslide assessment is vital for understanding and mitigating this natural hazard. ArcGIS and ENVI are powerful tools for this purpose.
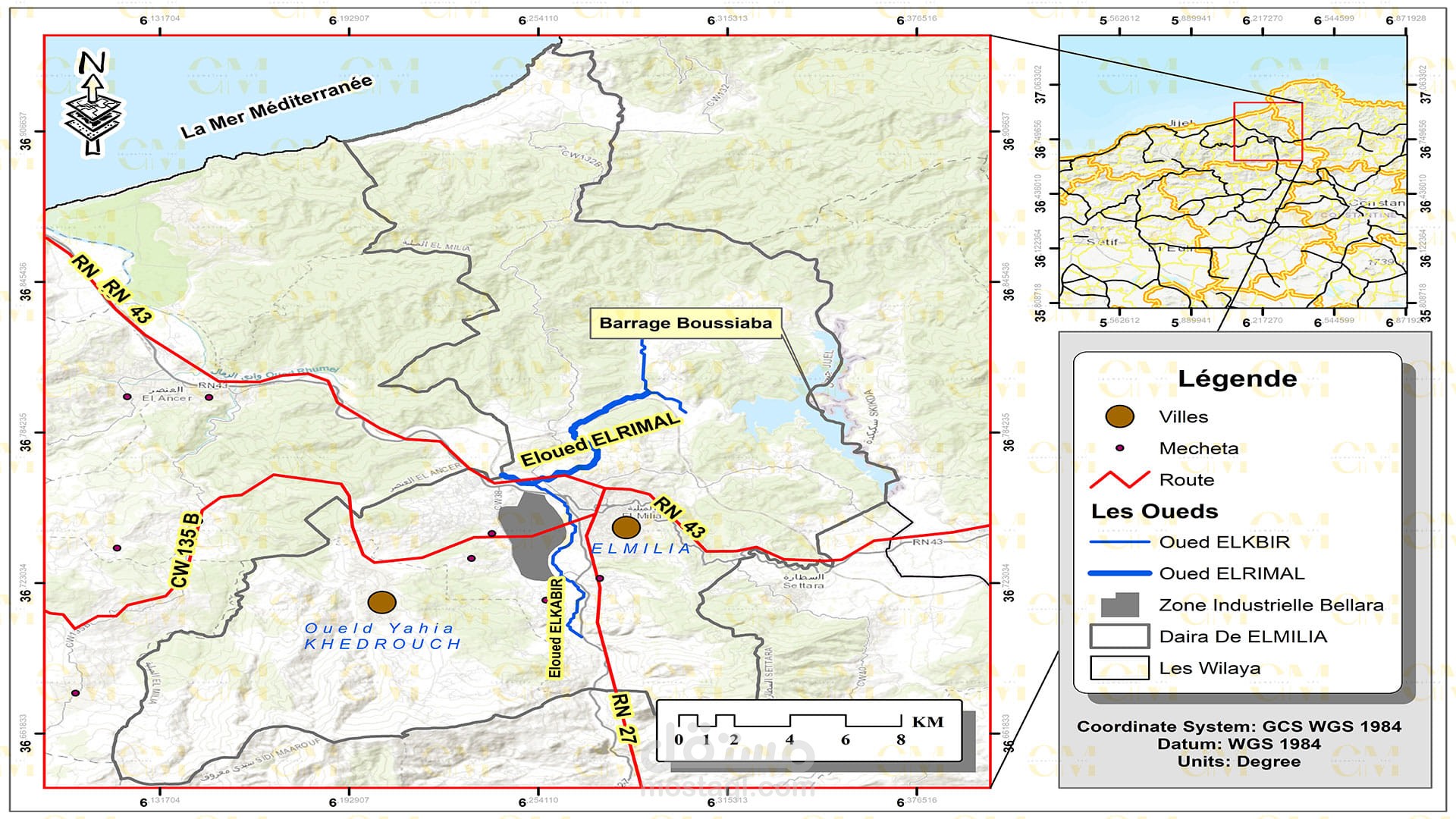
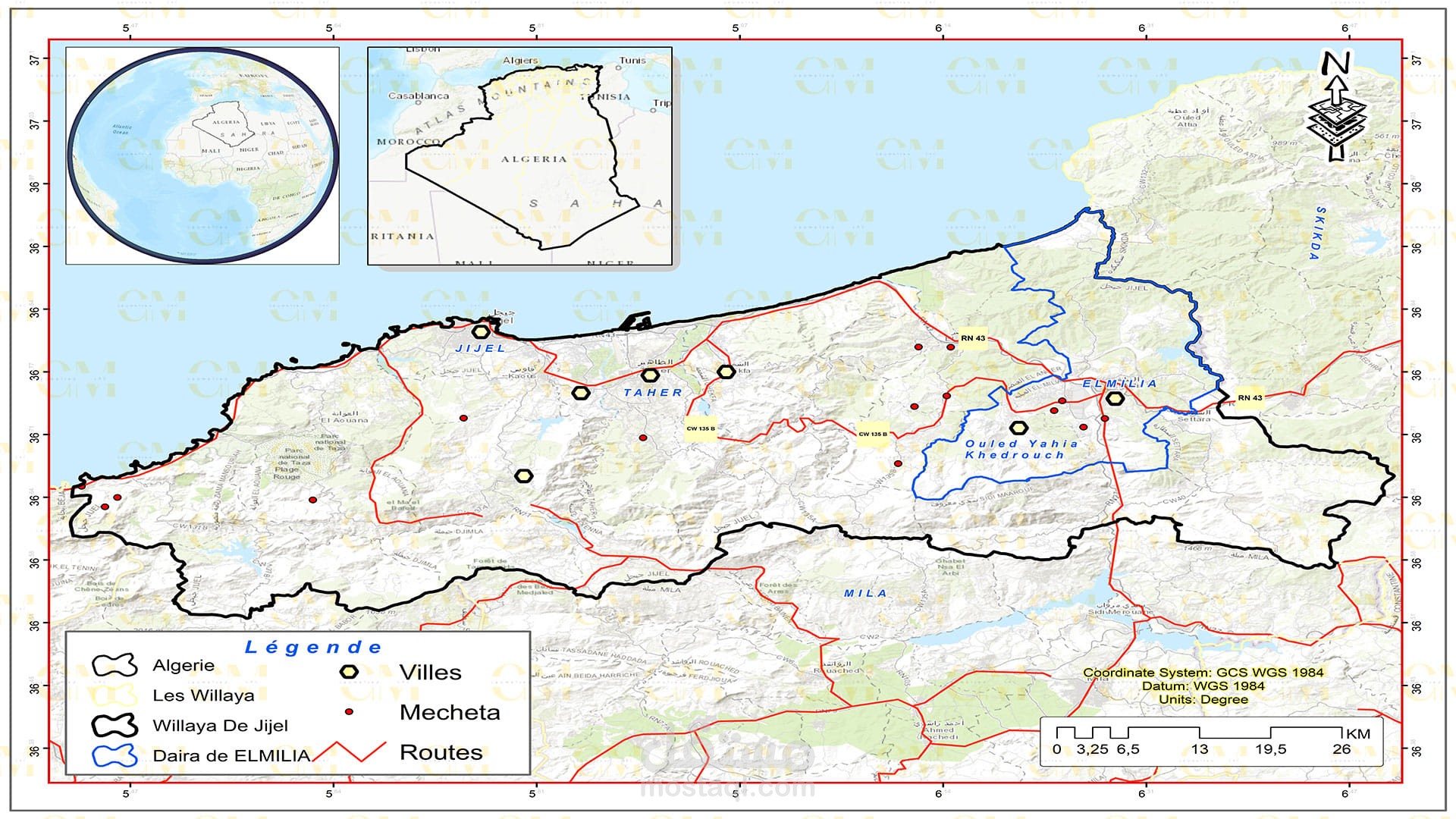
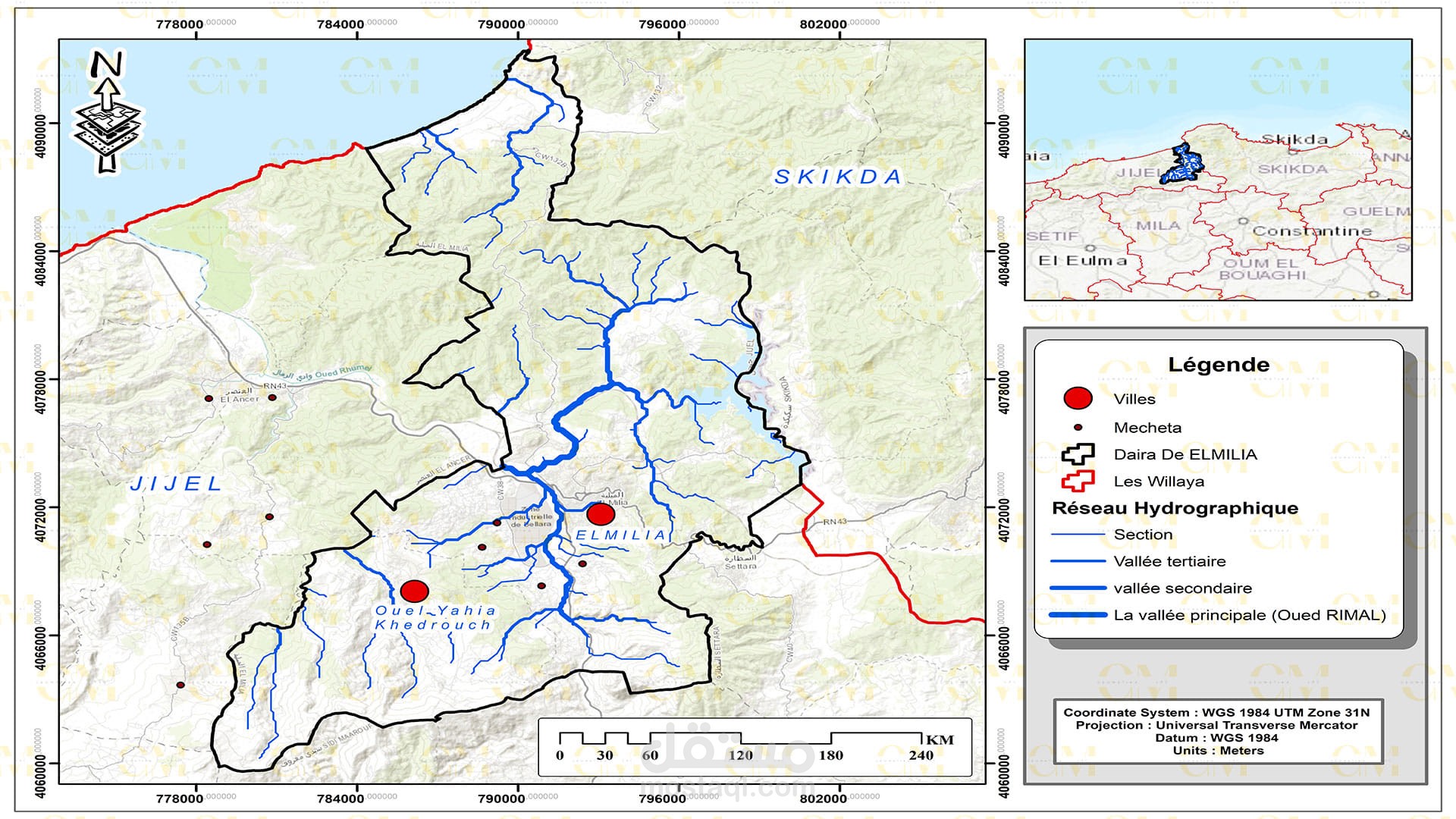
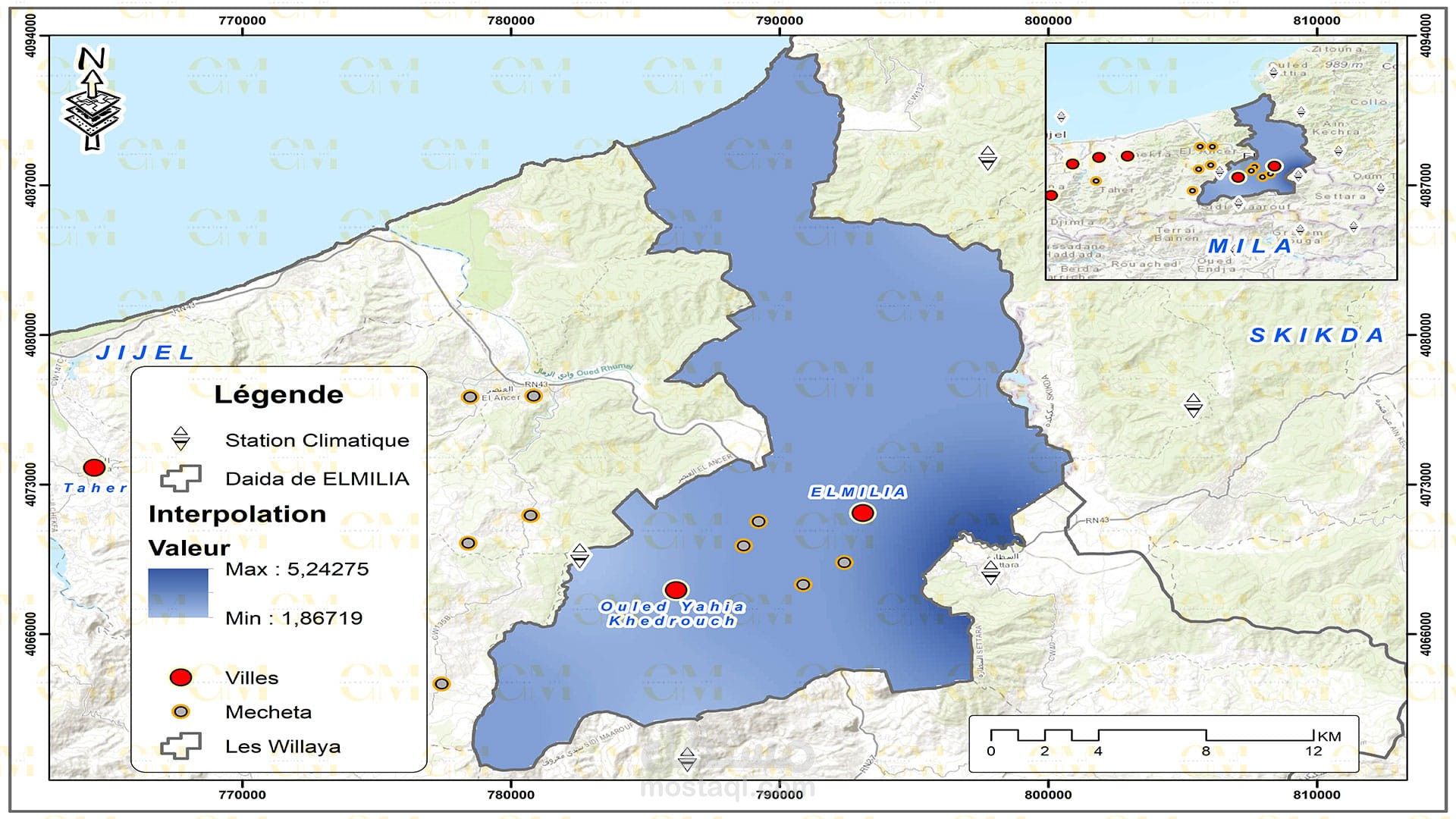
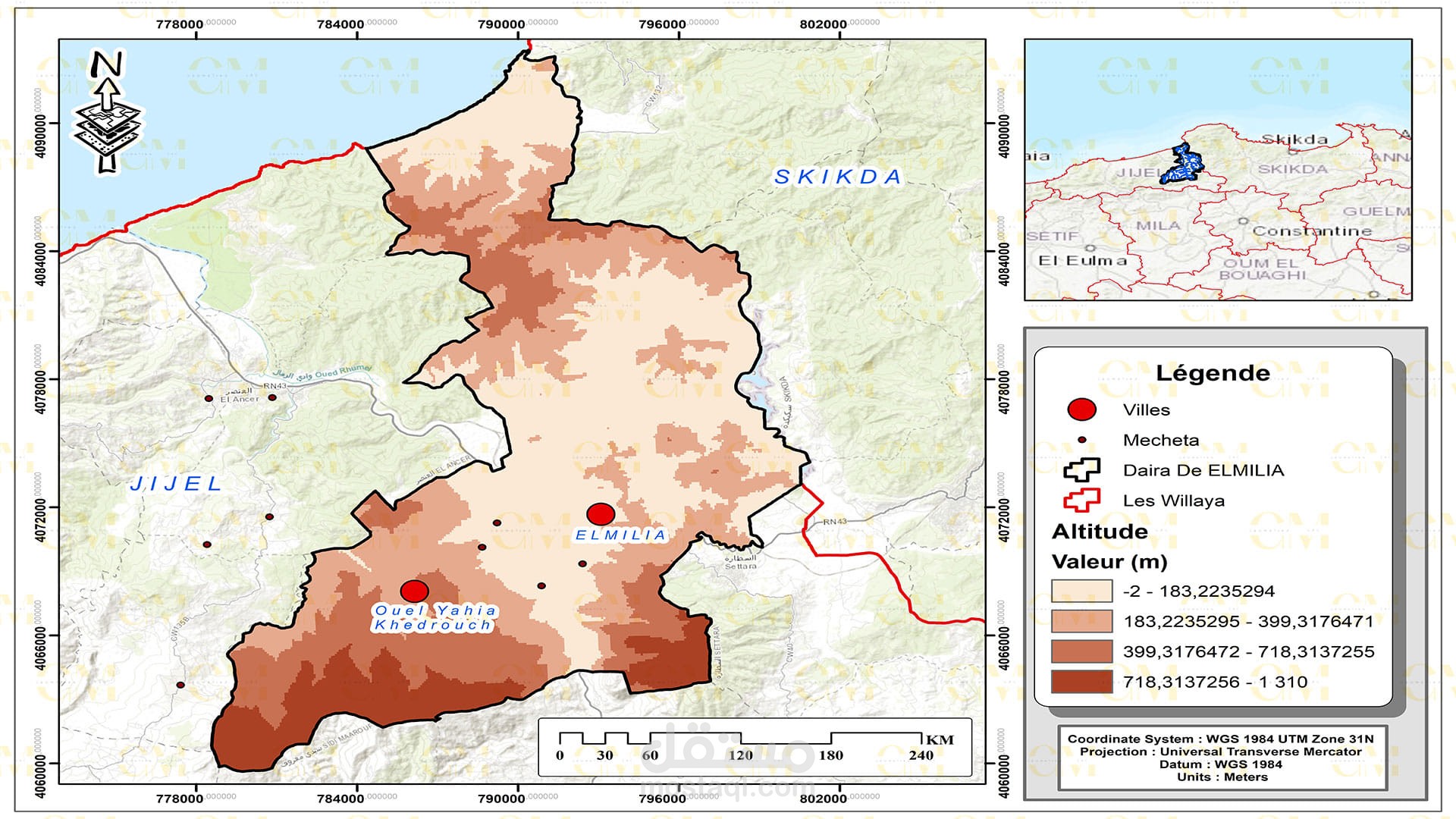
Data Collection: Remote sensing provides valuable data through satellite imagery and aerial photography. This data is integrated into GIS software like ArcGIS for further analysis.
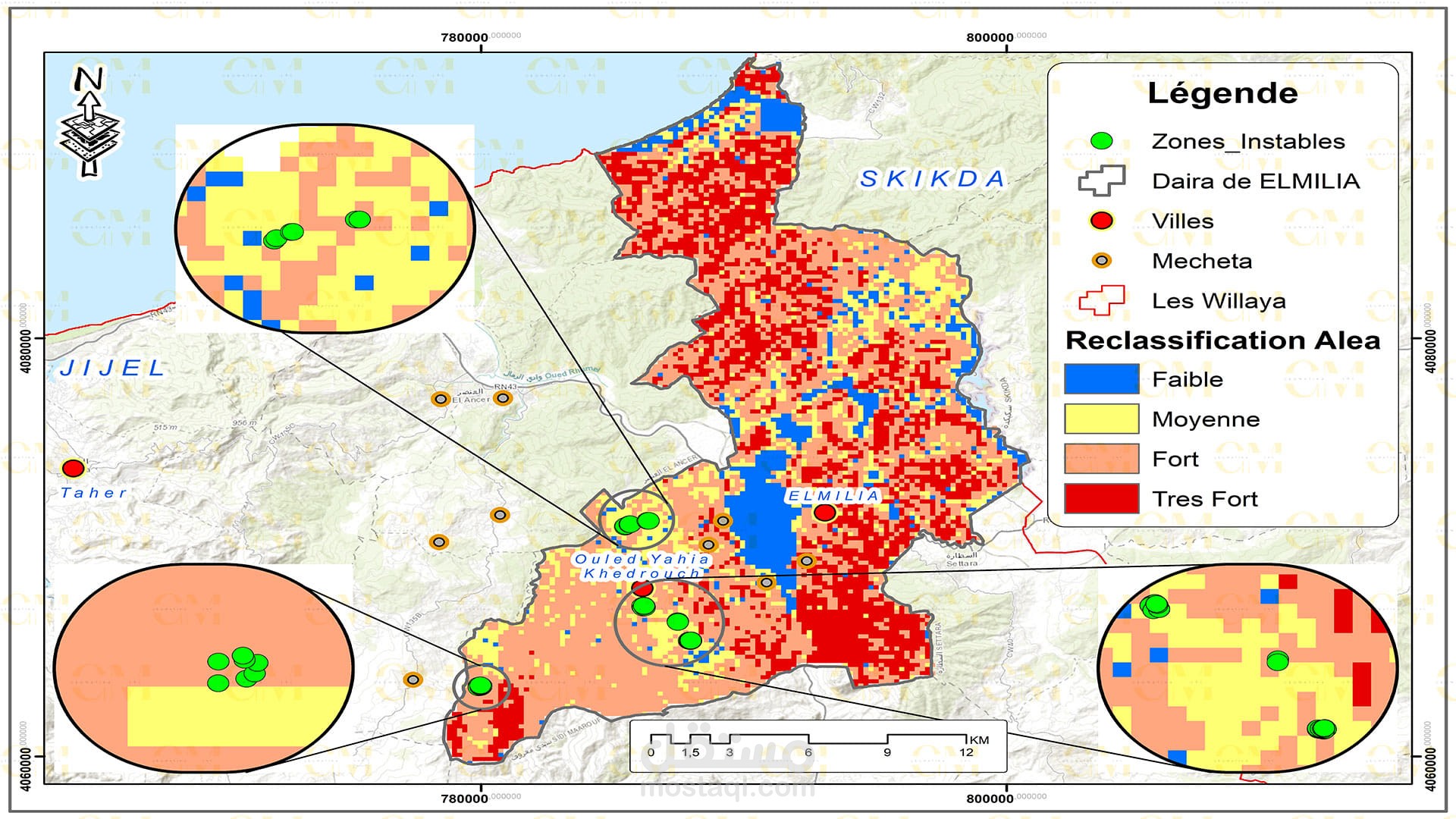
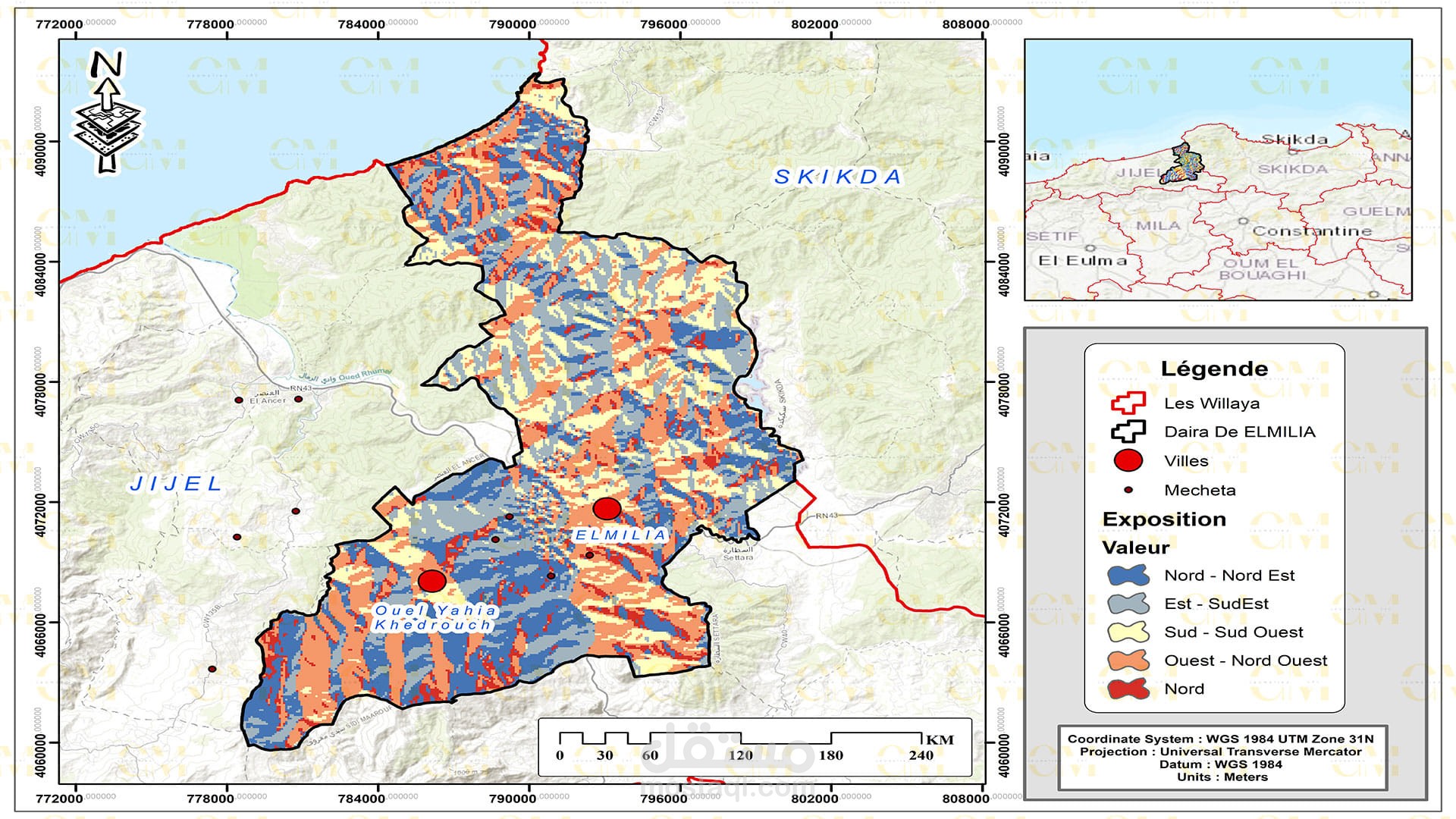
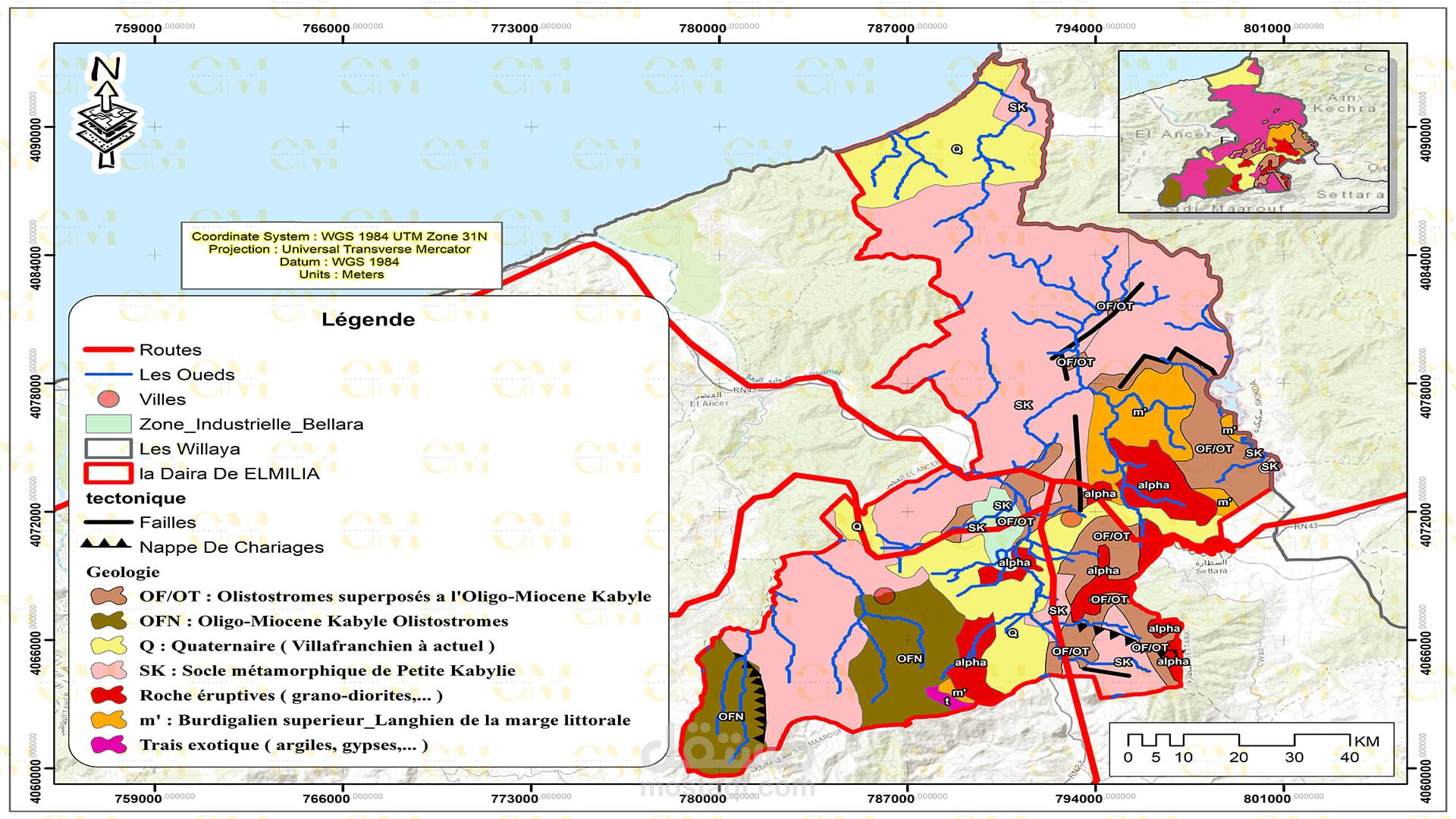
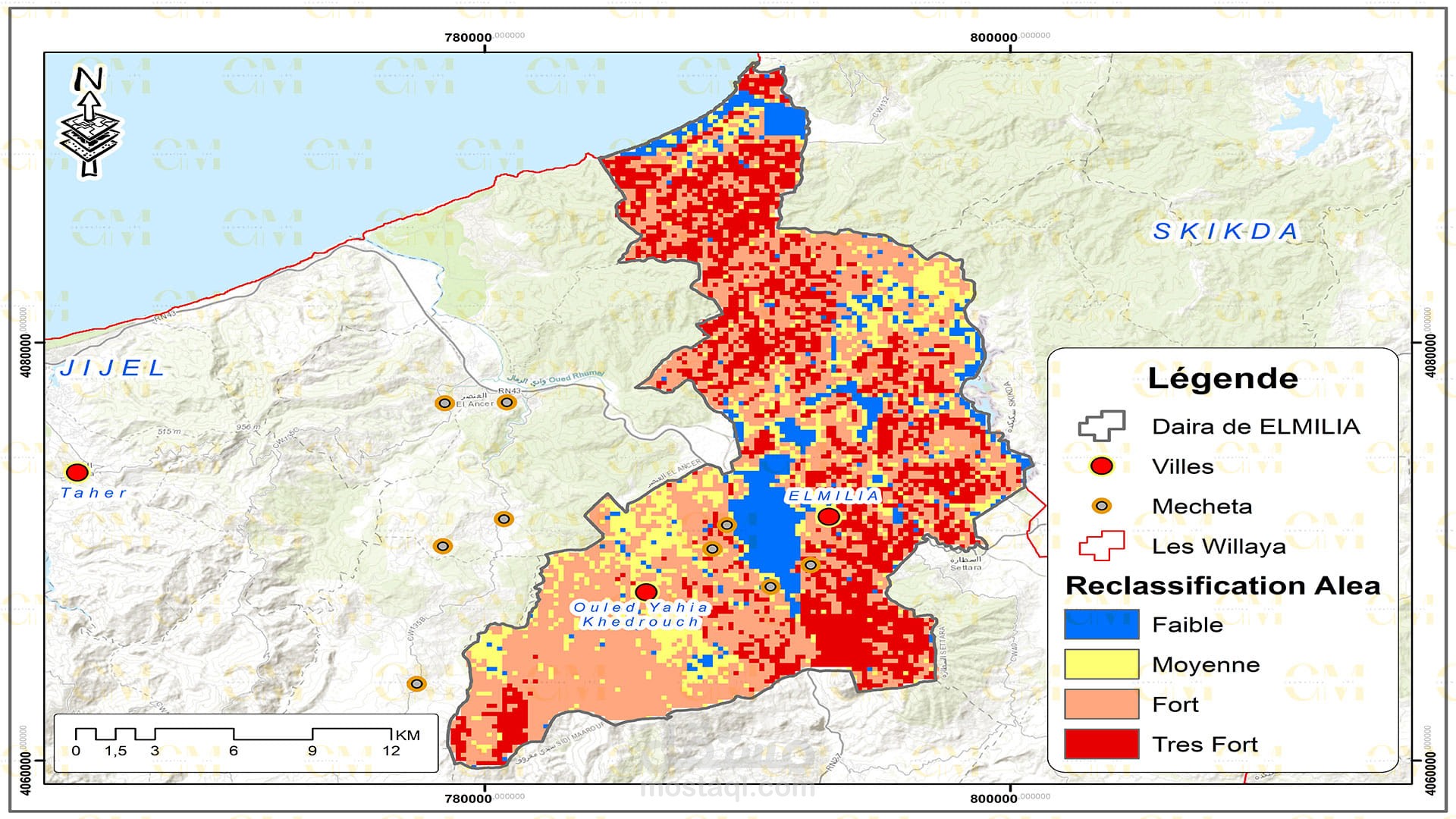
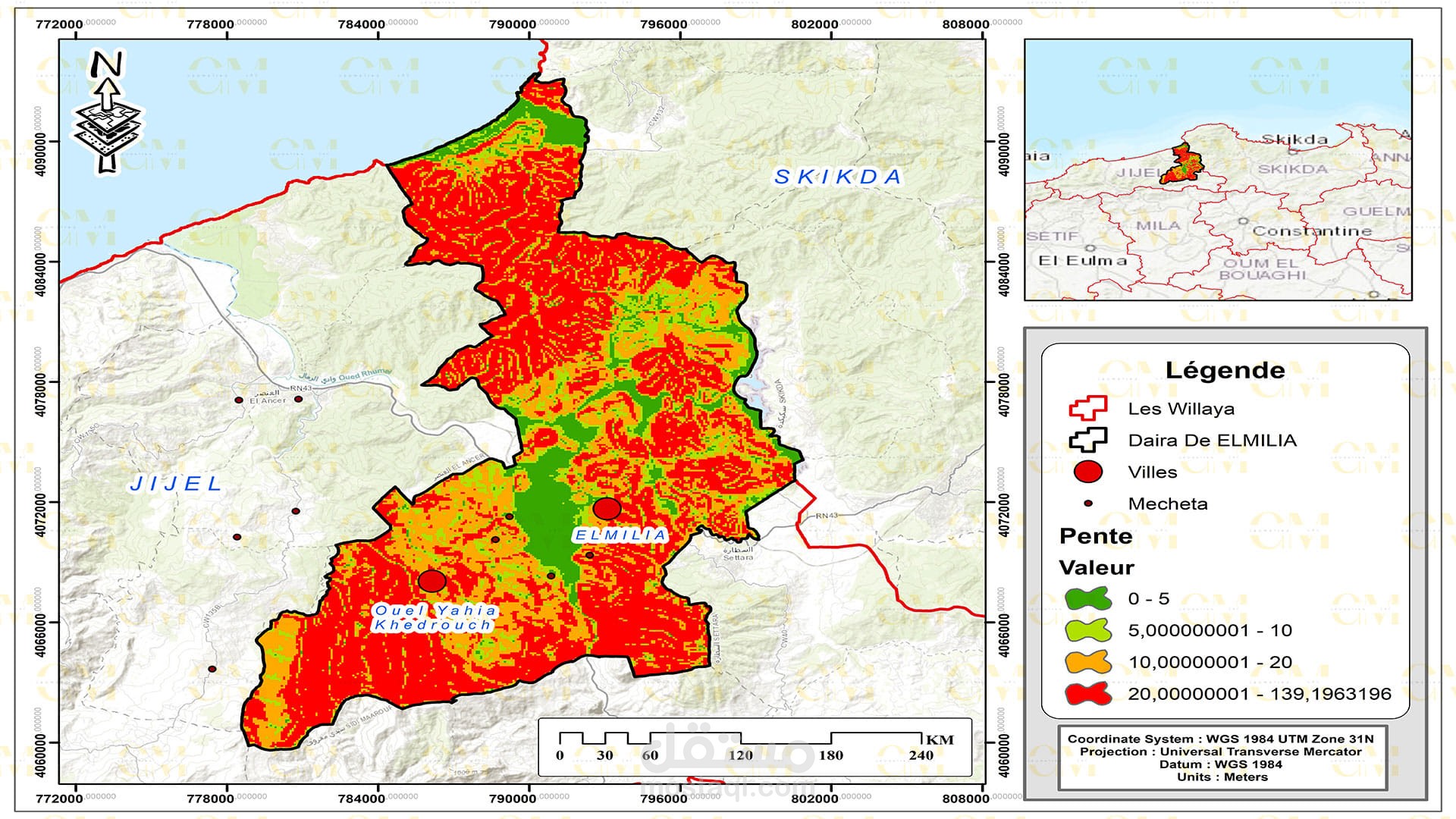
Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping helps identify areas prone to landslides. Various factors like topography, geology, rainfall, and land cover are analyzed to create susceptibility maps.
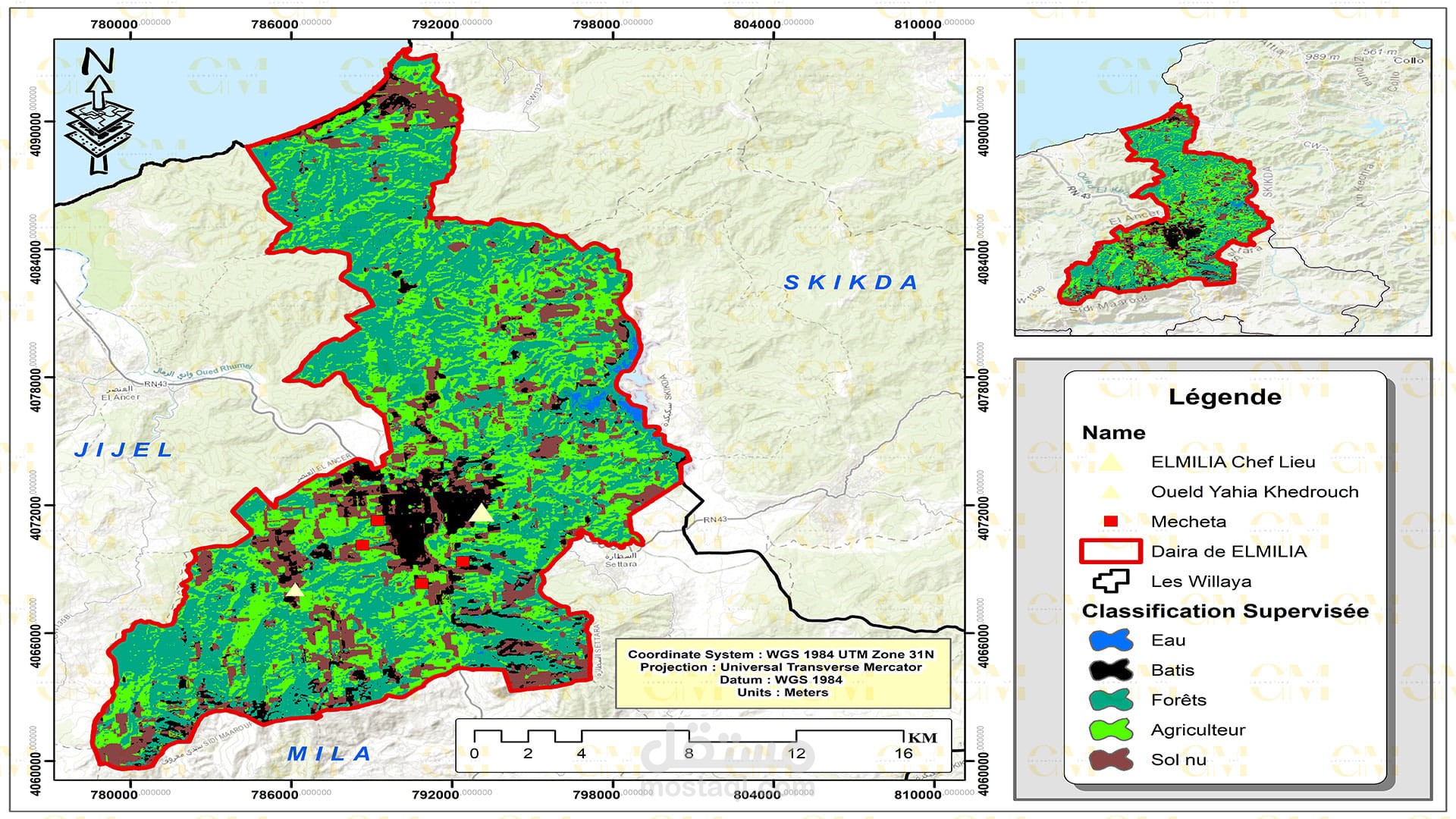
ENVI for Image Analysis: ENVI, a remote sensing software, is employed for in-depth image analysis. It aids in extracting valuable information from satellite imagery, such as land cover changes, soil moisture, and terrain characteristics.
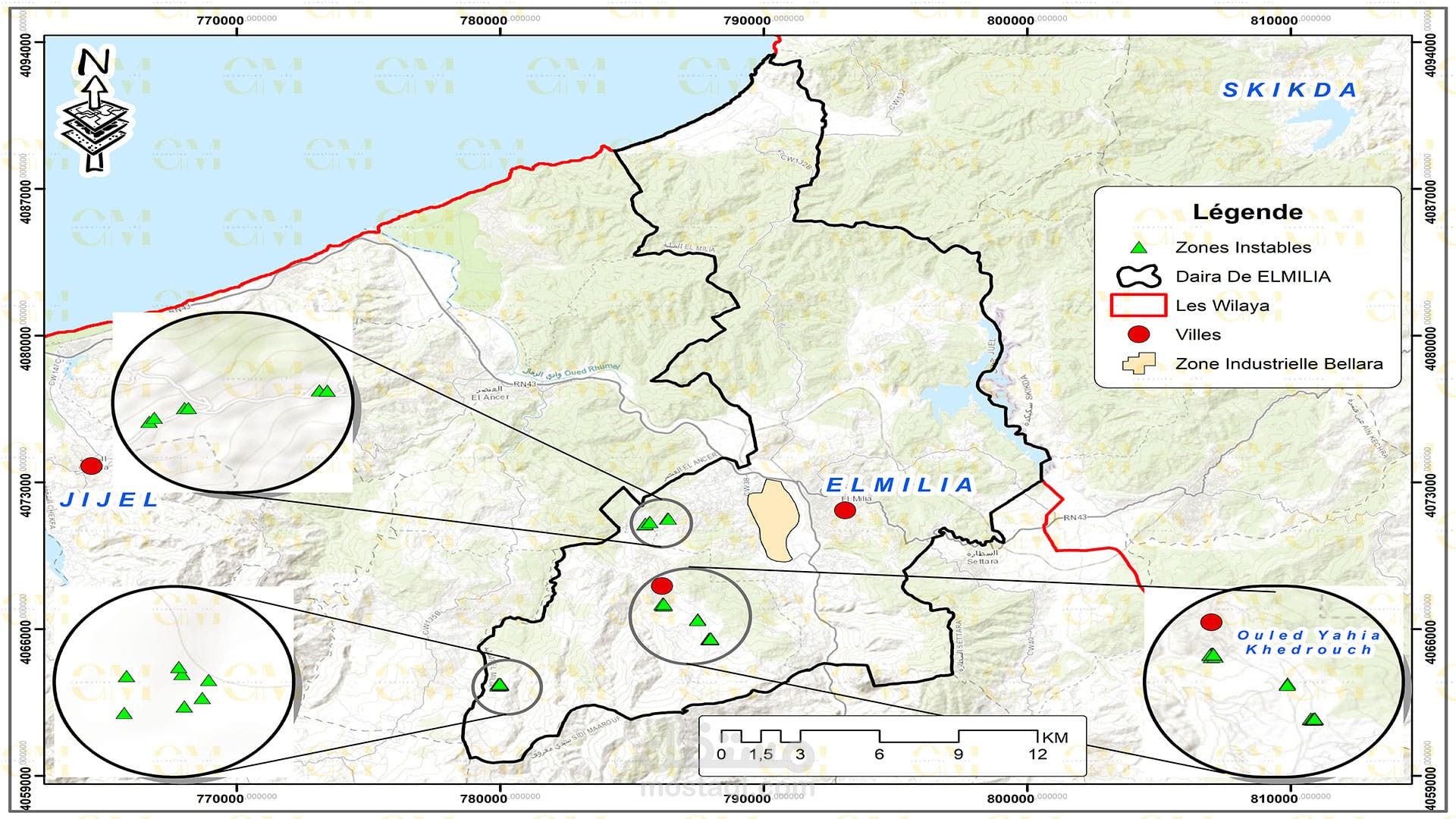
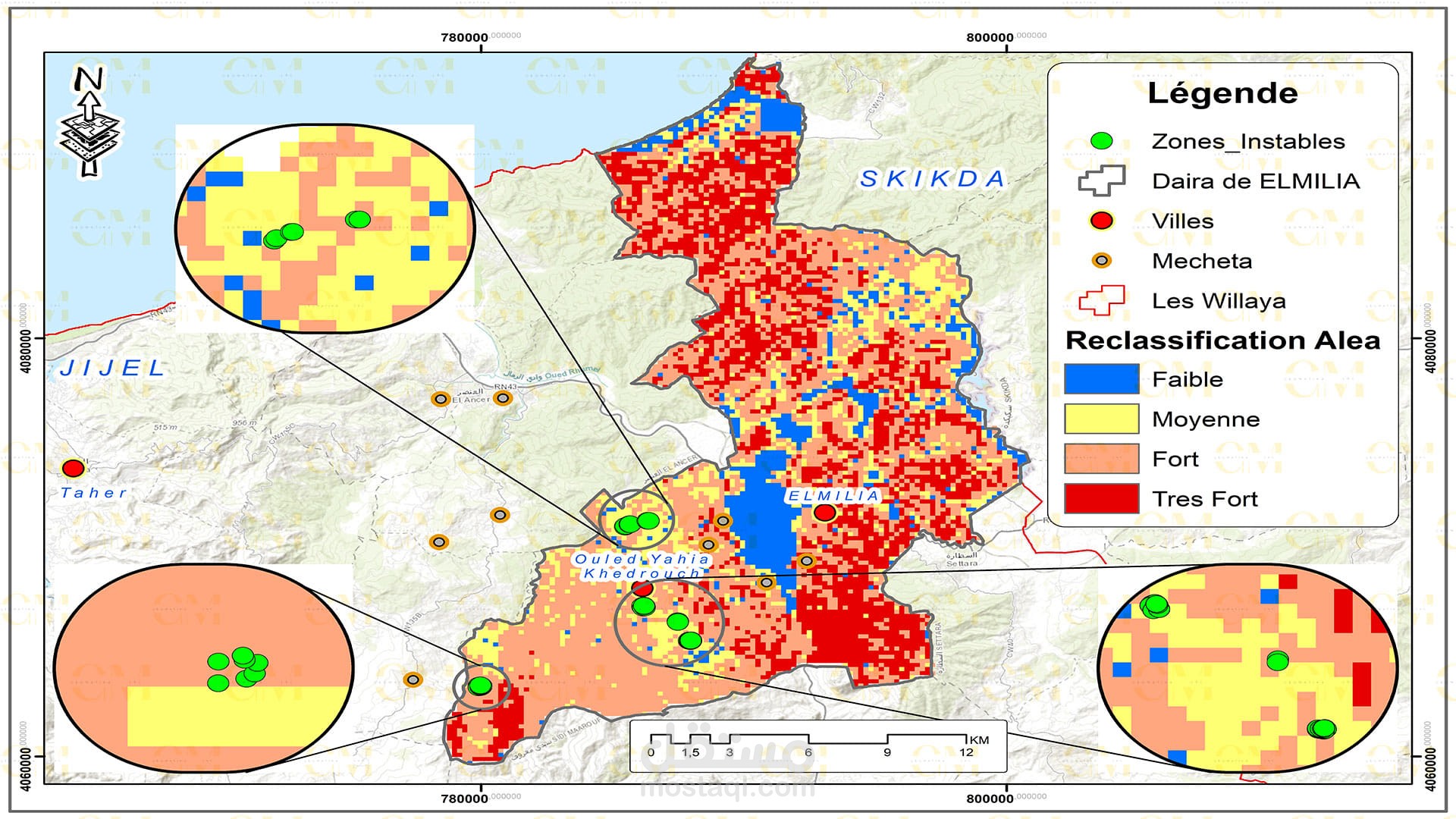
Risk Assessment: GIS allows geomatic engineers to assess the risk associated with landslides in specific regions. It helps prioritize preventive measures and disaster management planning.
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of landslide-prone areas is facilitated by remote sensing. Changes in terrain and land cover are detected, providing early warning signs.
Decision Support: GIS and remote sensing provide decision-makers with crucial information to plan infrastructure development and respond to landslide events effectively.
In summary, geomatic engineers use ArcGIS and ENVI in conjunction with remote sensing data to assess, monitor, and mitigate landslides. This integrated approach enhances our ability to understand and manage this geological hazard, ultimately reducing risks to communities and infrastructure.
بطاقة العمل
| اسم المستقل | حليم ر. |
| عدد الإعجابات | 0 |
| عدد المشاهدات | 23 |
| تاريخ الإضافة | |
| تاريخ الإنجاز |