Weather Prediction Using Machine Learning — Australia Weather Dataset
تفاصيل العمل
This project focuses on building a machine learning system to predict weather conditions using the Australian Weather Dataset (WeatherAUS). The notebook includes data cleaning, visualization, feature selection, and training multiple ML models to compare accuracy and performance.
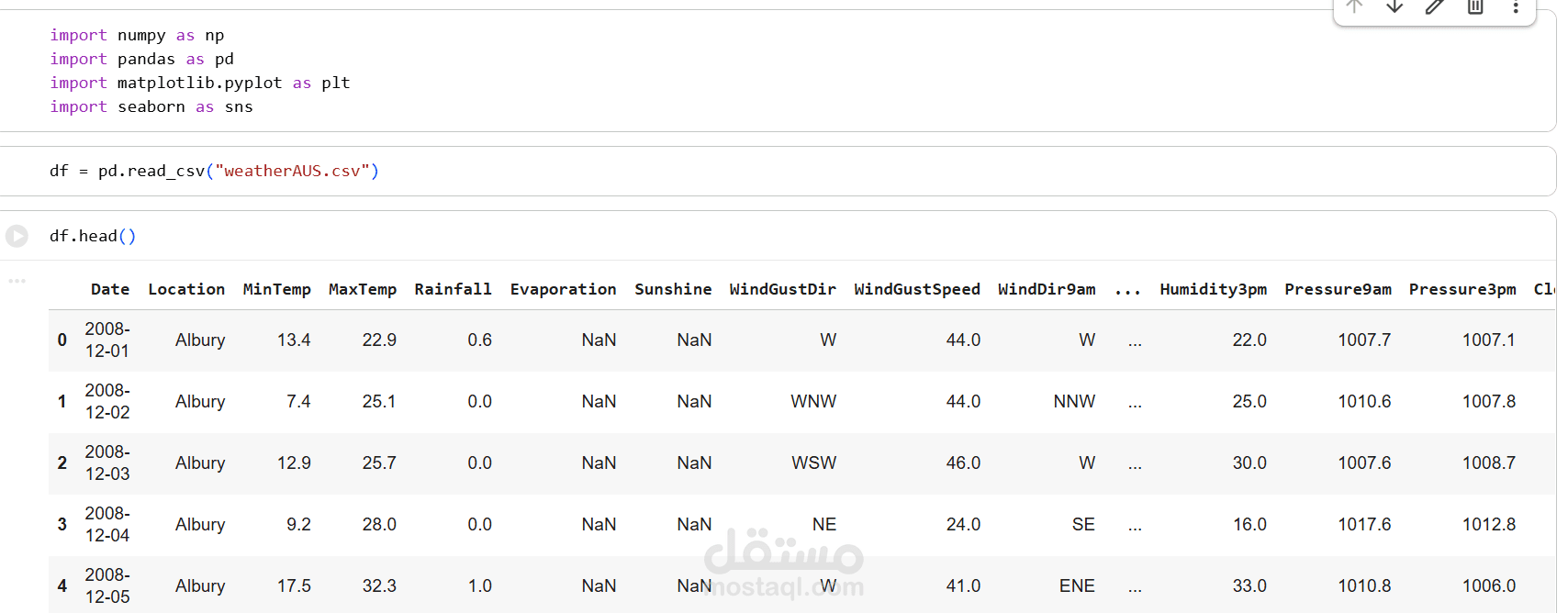
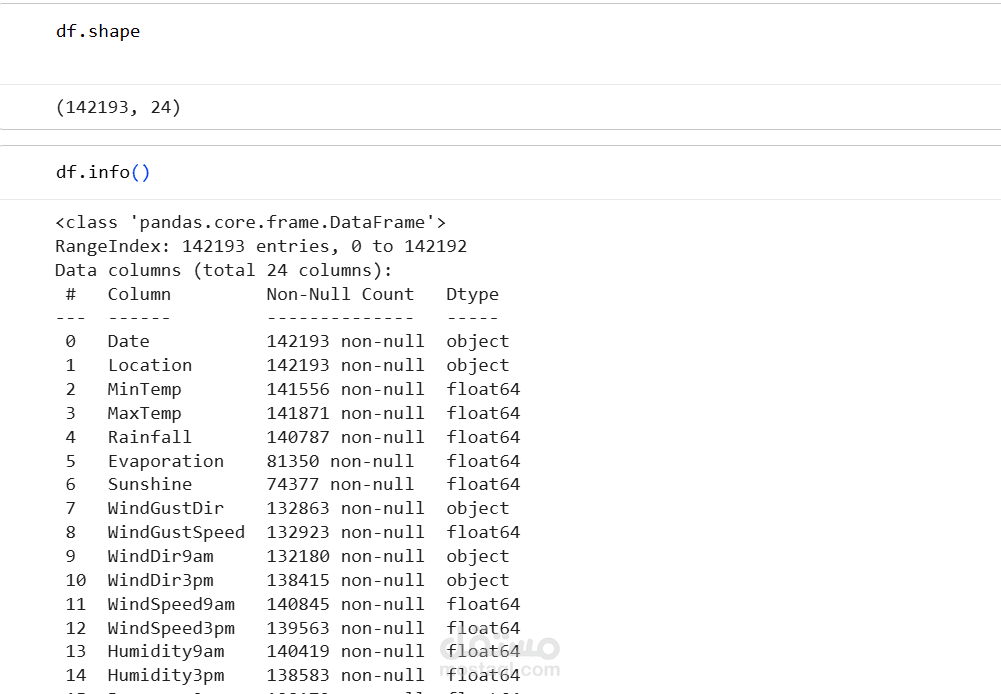
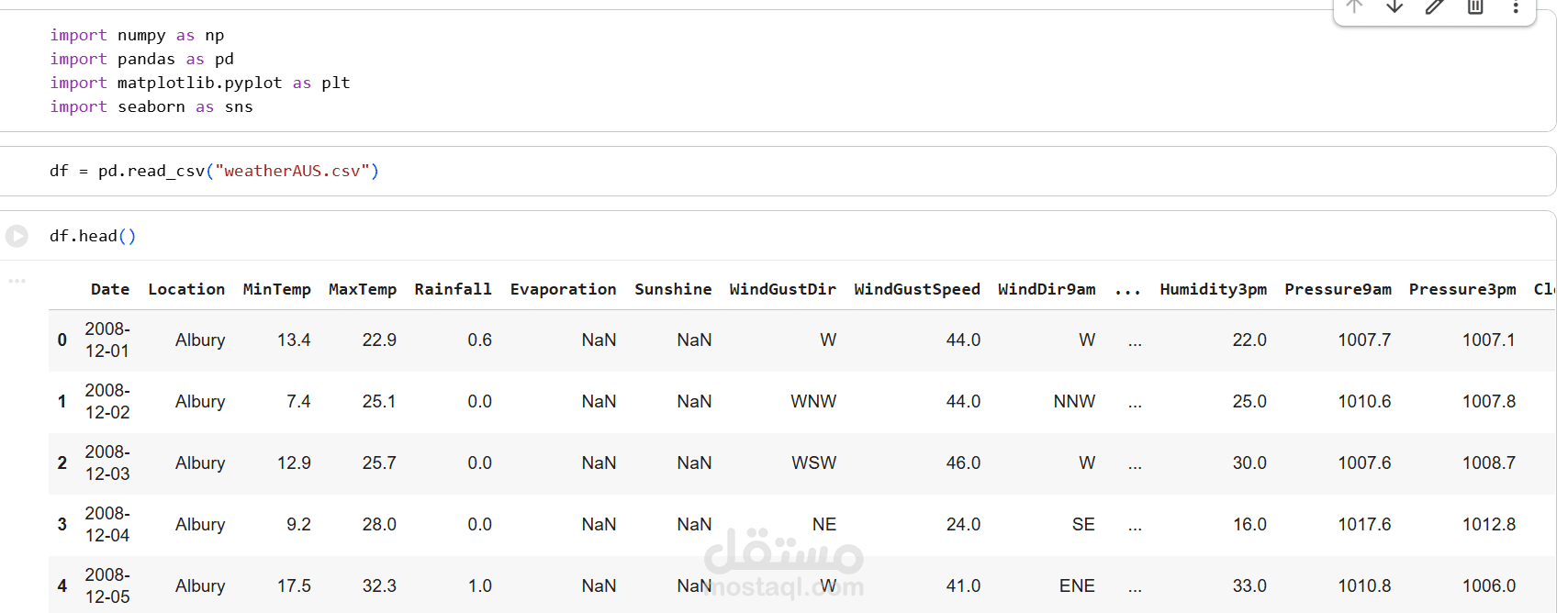
1. Dataset
The dataset contains historical weather data collected across multiple Australian locations.
Includes features such as temperature, humidity, pressure, rainfall, wind speed, cloud cover, and more.
The target variable typically predicts whether it will rain tomorrow (binary classification).
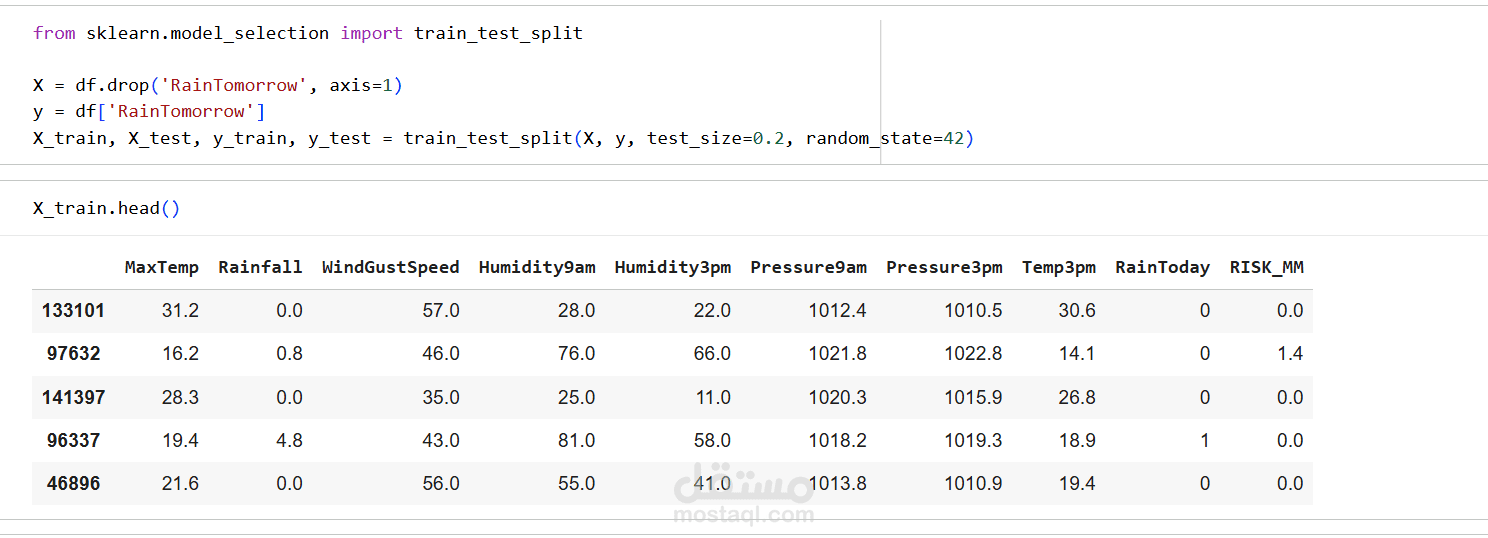
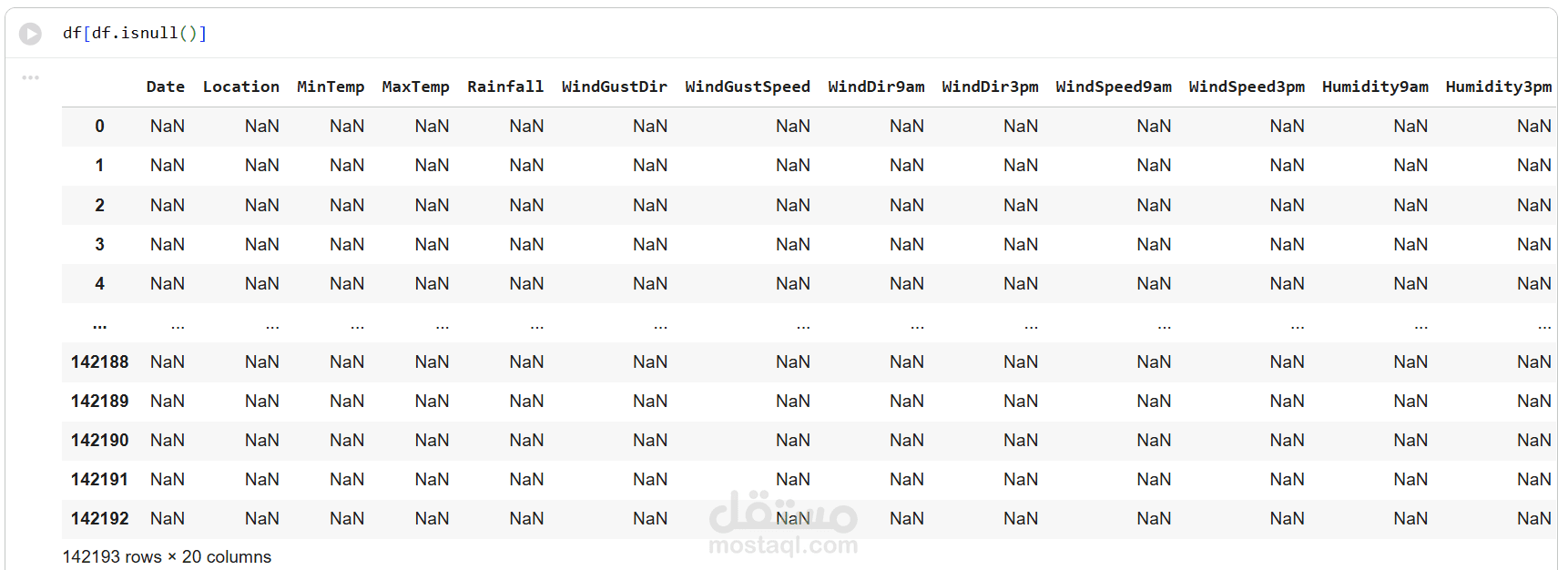
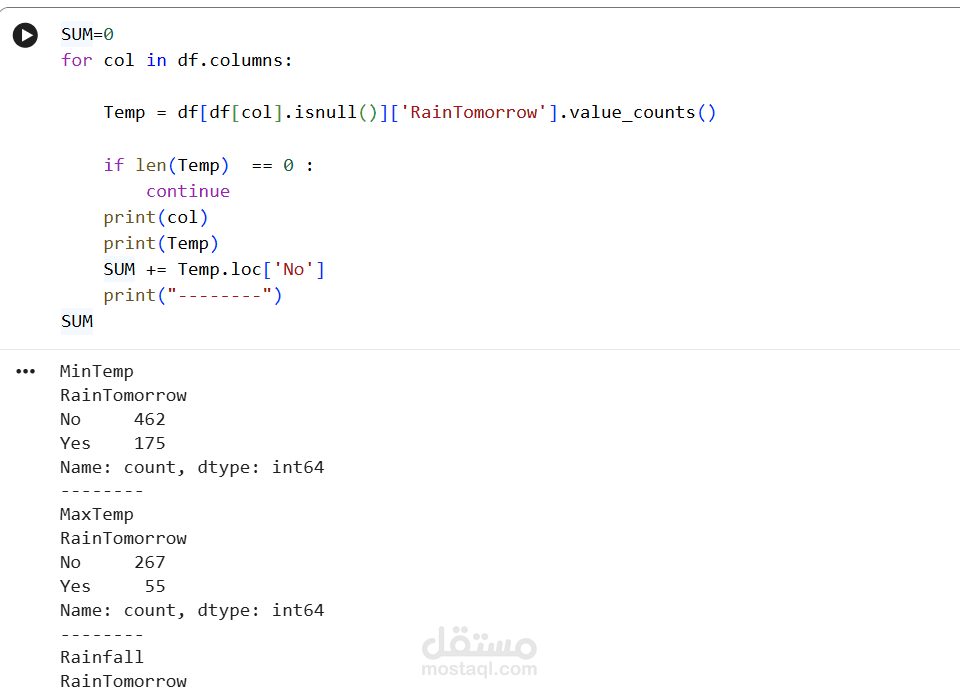
2. Preprocessing Steps
Handling missing values
Converting categorical values into numerical encoding
Splitting dataset into features (X) and labels (y)
Normalizing/standardizing numerical columns
Preparing the data for machine learning models
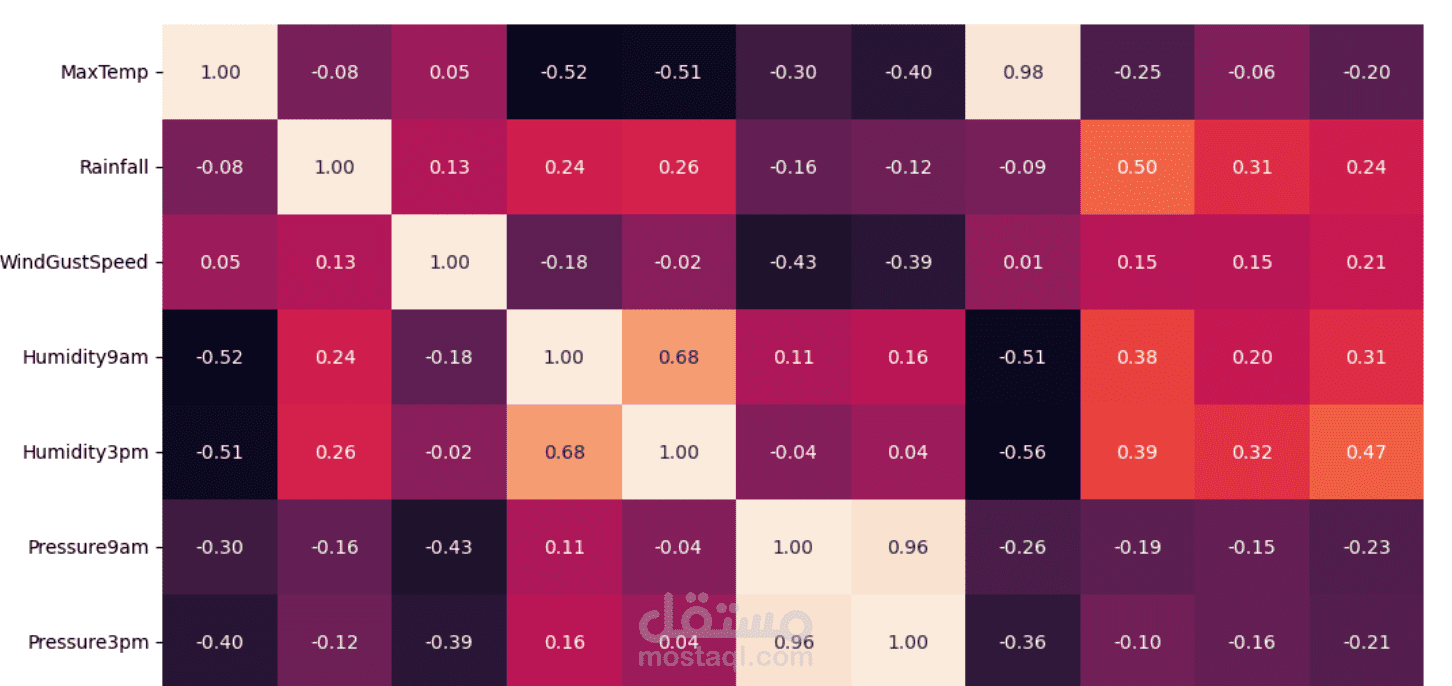
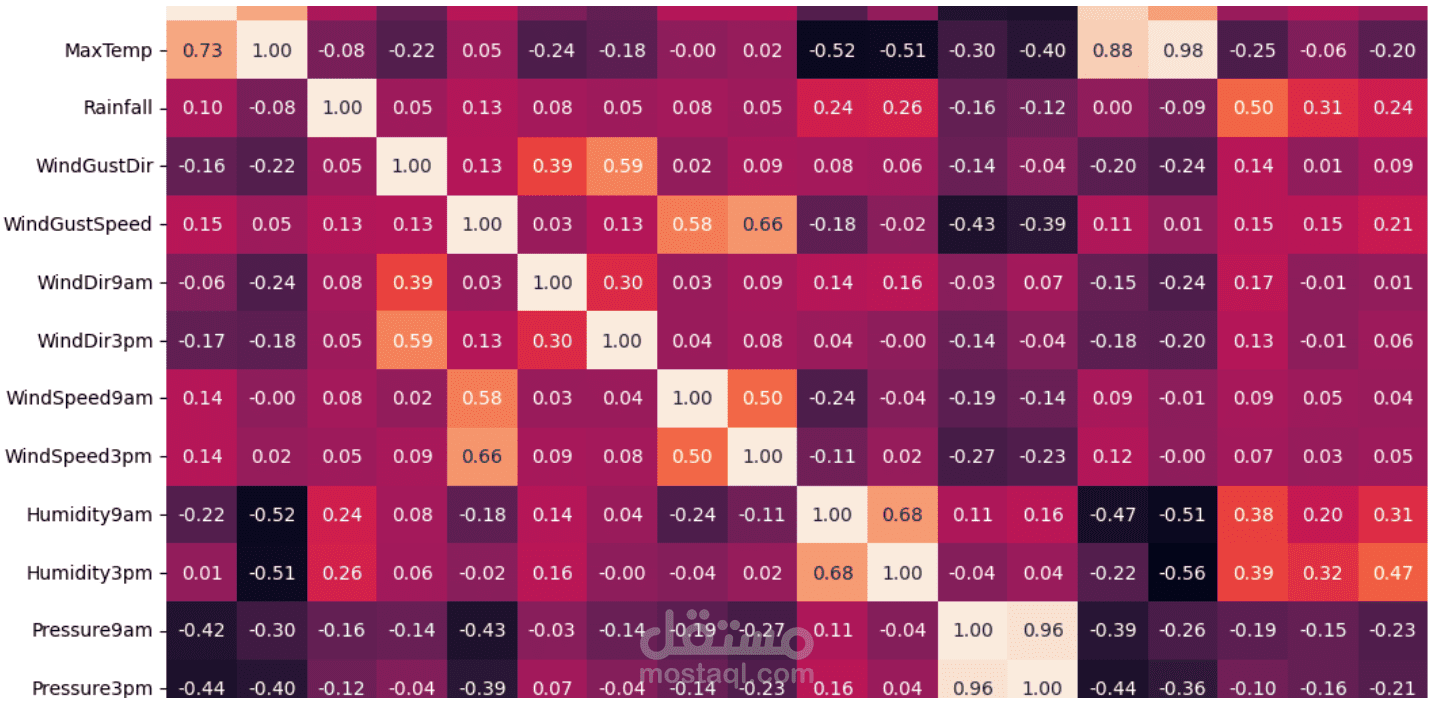
3. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Visualizing variable distributions
Checking correlations between weather features
Identifying patterns that influence rainfall
Plotting graphs for temperature, humidity, rainfall, etc.
4. Machine Learning Models Used
The project trains and evaluates multiple ML models, including:
Logistic Regression
Random Forest Classifier
Decision Trees
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
Naive Bayes
Each model is tested on unseen data to measure prediction accuracy.
5. Model Evaluation
The notebook includes evaluation using:
Accuracy
Precision
Recall
F1-score
Confusion Matrix
Classification Report
These metrics help identify which algorithm performs best for weather prediction.
6. Summary
This project demonstrates how machine learning can be applied to climate data for predictive weather analysis. It includes a full pipeline from raw dataset → preprocessing → EDA → ML training → evaluation.
The system can be extended for real-time forecasting and integrated into smart agriculture or climate monitoring applications.