AWS Lex Translation Chatbot
تفاصيل العمل
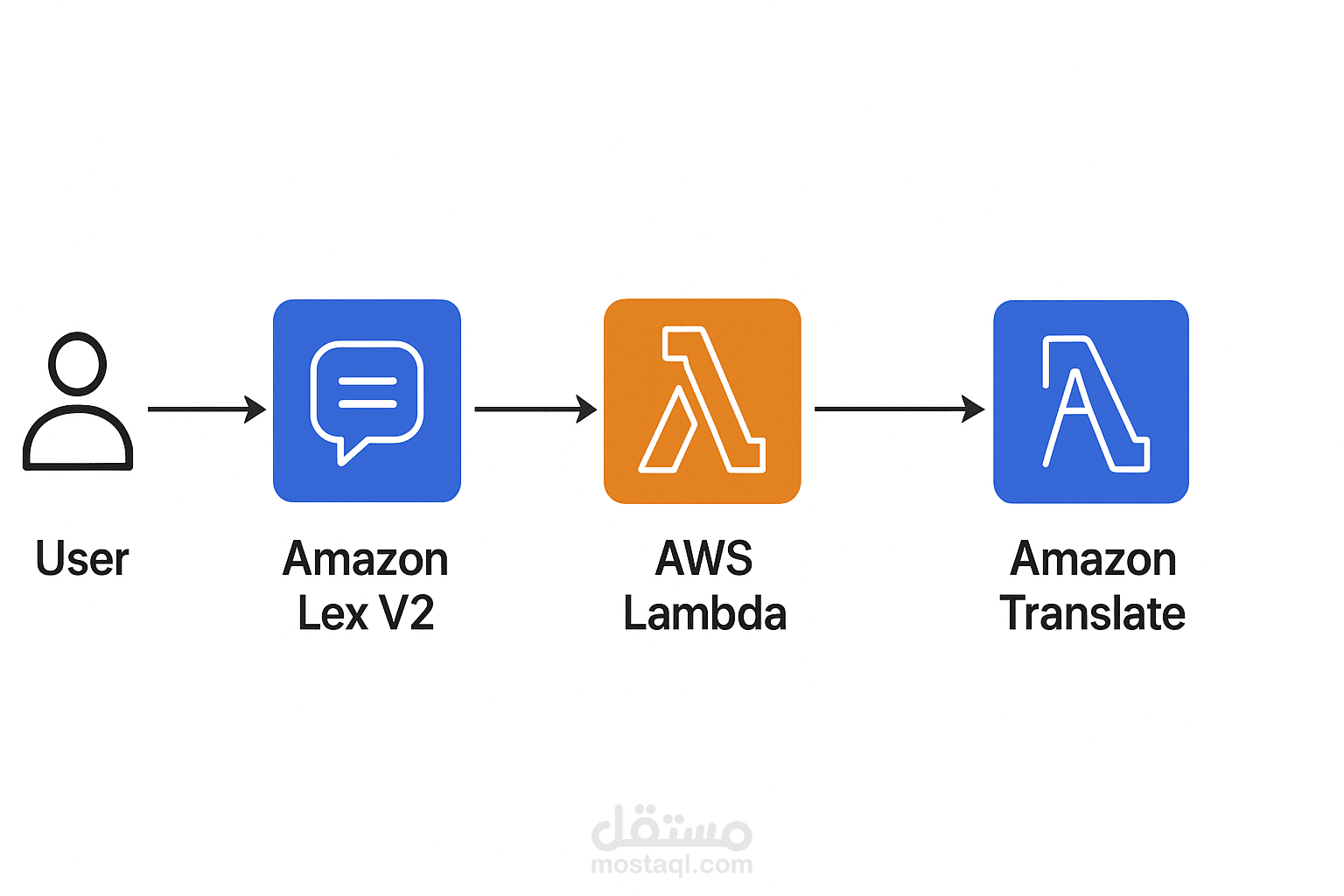
Architecture
Amazon Lex V2 – captures user input and manages intents.
AWS Lambda – processes input, extracts text and target language, calls Amazon Translate, and returns a response.
Amazon Translate – performs real-time translation.
ChatGPT Image Sep 6, 2025, 12_41_04 PM
Prerequisites
AWS account (Free Tier covers Lex, Lambda, Translate usage at low volume).
IAM user with rights to create/manage Lex, Lambda, Translate, and IAM roles.
Python 3.9+ runtime for Lambda.
Step 1: IAM Setup
Go to IAM → Roles → Create Role.
Select Lambda as trusted entity.
Attach these policies:
AmazonLexFullAccess
AmazonTranslateFullAccess
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole (for CloudWatch logging)
Name it: LexTranslateLambdaRole.
? Step 2: Create the Lex V2 Bot
Open Amazon Lex V2 Console → Create bot.
Name: TranslateBot.
Select: Custom bot.
Language: English (US).
IAM Role: use the default Lex role (auto-created).
Create an alias (e.g., TestBotAlias).
? Step 3: Create Intent
Go to your bot → Intents → Add intent → Create intent.
Name: TranslateIntent.
Add slot:
Name: TargetLanguage
Slot type: AMAZON.Language
Required: Yes
Prompt: "Which language should I translate to?"
Add sample utterances:
translate {TargetLanguage}
translate hello to {TargetLanguage}
please translate this to {TargetLanguage}
Leave SourceText out (cannot use FreeFormInput in utterances).
️ Step 4: Create Lambda
Go to AWS Lambda → Create function.
Name: TranslateLambda.
Runtime: Python 3.9.
Role: LexTranslateLambdaRole.
Paste the following code:
import boto3
translate = boto3.client('translate')
LANGUAGE_MAP = {
"arabic": "ar",
"chinese": "zh",
"english": "en",
"french": "fr",
"german": "de",
"hindi": "hi",
"italian": "it",
"japanese": "ja",
"korean": "ko",
"portuguese": "pt",
"russian": "ru",
"spanish": "es",
}
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print("Event:", event)
slots = event['sessionState']['intent'].get('slots', {})
user_input = event.get("inputTranscript", "")
# Get target language
if slots and slots.get('TargetLanguage'):
target_language = slots['TargetLanguage']['value']['interpretedValue'].lower()
else:
target_language = "english"
# Extract source text (strip keywords like "translate" and "to <language>")
source_text = user_input.lower().replace("translate", "").strip()
if " to " in source_text:
source_text = source_text.split(" to ")[0].strip()
# Map language to Translate code
target_lang_code = LANGUAGE_MAP.get(target_language, "en")
# Translate
response = translate.translate_text(
Text=source_text,
SourceLanguageCode="auto",
TargetLanguageCode=target_lang_code
)
translated_text = response['TranslatedText']
return {
"sessionState": {
"dialogAction": {"type": "Close"},
"intent": {
"name": "TranslateIntent",
"state": "Fulfilled"
}
},
"messages": [
{
"contentType": "PlainText",
"content": f"The translation in {target_language.title()} is: {translated_text}"
}
]
}
Deploy the Lambda.
Step 5: Attach Lambda to Lex
In Lex Console → Intents → TranslateIntent → Fulfillment.
Choose Lambda function → select TranslateLambda.
Save and Build the bot.
? Step 6: Test
Go to Test window in Lex console.
Try:
translate hello to german
Response:
The translation in German is: Hallo
Try sentences:
translate how are you today to french
Response:
The translation in French is: Comment allez-vous aujourd'hui ?
Debugging
If you only see Intent fulfilled → check Lambda return JSON format (must include messages).
If Lambda isn’t invoked → check fulfillment settings and add a resource-based policy to Lambda:
aws lambda add-permission \
--function-name TranslateLambda \
--action lambda:InvokeFunction \
--principal lexv2.amazonaws.com \
--statement-id lex-translate-invoke \
--source-arn arn:aws:lex:us-east-1:ACCOUNT_ID:bot-alias/BOT_ID/ALIAS_ID
Use CloudWatch Logs to debug Lambda errors.
Notes
Supports sentences, not just words (limit: ~5000 characters).
Free Tier covers:
Lex: 10,000 text requests/month for 12 months
Translate: 2M characters/month for 12 months