Covid-19 Radiology
تفاصيل العمل
This project applies deep learning to detect COVID-19 from chest radiographs (X-ray images). It uses the COVID-19 Radiography Database from Kaggle, which contains chest X-ray images of patients with COVID-19, viral pneumonia, and normal (healthy) cases.
Goal
The goal of the project is to build a reliable image classification model that can distinguish COVID-19 cases from other conditions, achieving high performance with a balanced trade-off between precision and recall.
Approach
- Data Preparation
- Load and preprocess the COVID-19 Radiography Database.
- Resize and normalize images.
- Apply data augmentation (rotations, flips, etc.) to reduce overfitting and improve generalization.
Model Development
- Use VGG19, a pre-trained convolutional neural network, through transfer learning.
- Replace the top layers with a custom classification head suited to the dataset classes.
- Fine-tune the network on the radiology dataset.
Training
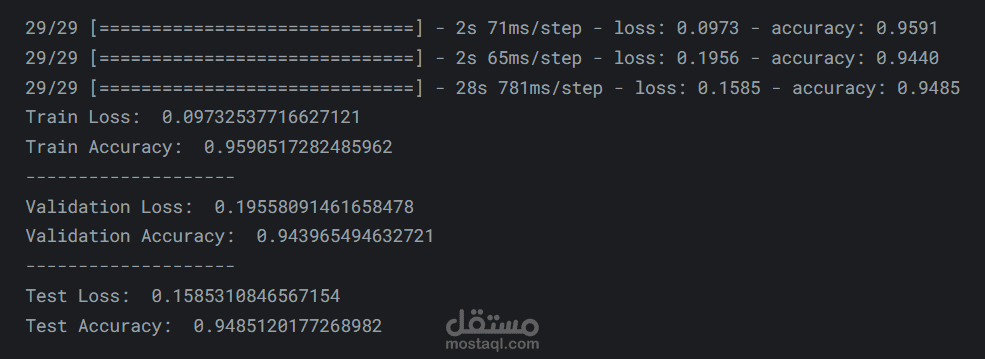
- Split data into training, validation, and test sets.
- Train with suitable hyperparameters (batch size, learning rate, epochs).
- Use callbacks such as early stopping and learning rate scheduling.
Evaluation
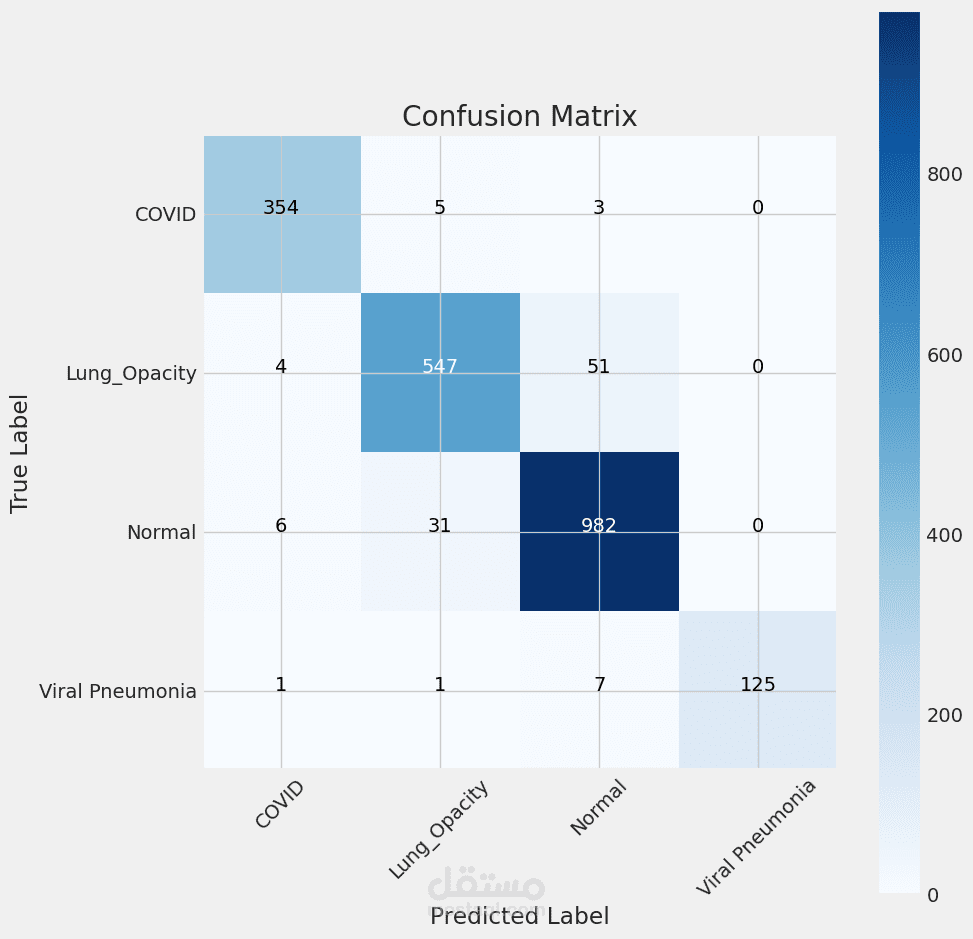
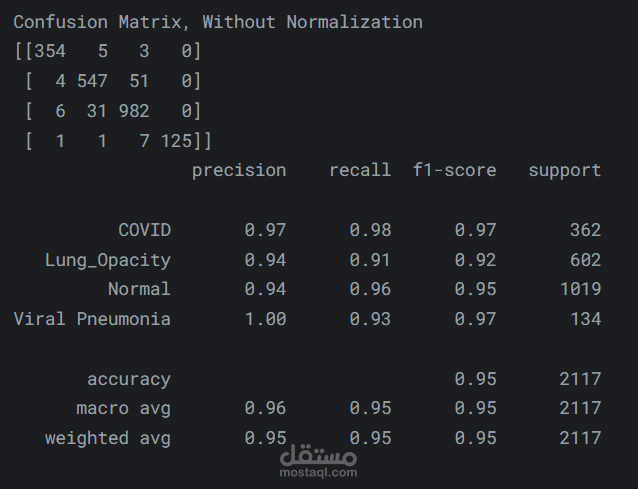
- Assess the model using metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and confusion matrix.
- Achieved an F1-score of 95%, showing strong and balanced classification performance.
Outcomes
- High performance: The project demonstrates that transfer learning with VGG19 is effective for COVID-19 radiology classification.
- Reproducibility: Uses a well-known dataset, enabling others to replicate and extend the results.
- Practical Relevance: Highlights the potential of deep learning to support medical diagnosis in radiology, though real-world deployment would require clinical validation.