PRINCIPALE SUPPORT ANALYSIS - تحليل الدعامة الرئيسية
تفاصيل العمل
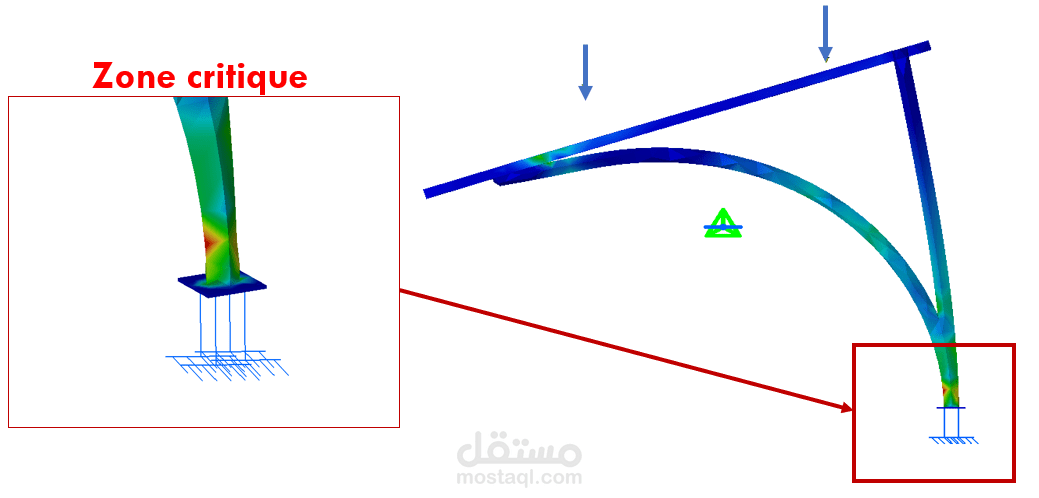
يُعد تحليل الدعامة الرئيسية خطوة محورية في تقييم قدرة هذا العنصر الهيكلي على تحمّل الأحمال المختلفة المطبقة عليه أثناء التشغيل. يتم التحليل باستخدام تقنيات العناصر المنتهية (FEM) من أجل محاكاة الاستجابة الفيزيائية للمادة والهندسة تحت تأثير القوى الخارجية، مثل الوزن الذاتي، الحمل الناتج عن التجهيزات المرتبطة، والرياح.
تم تنفيذ التحليل على الدعامة باستخدام برنامج CATIA V5، عبر وحدة Generative Structural Analysis، التي تتيح تطبيق أحمال موزعة أو مركّزة، وتحديد شروط التثبيت والدعم (encastrements). خلال التحليل، يتم حساب:
الإجهادات (Contraintes)، وخاصة إجهاد فون ميسز (von Mises)، لتحديد ما إذا كانت الدعامة معرضة للفشل تحت الأحمال المركبة.
التشوهات (Déformations)، لمعرفة ما إذا كان الانحناء أو التمدد ضمن الحدود المسموح بها.
نقاط التركيز الحرجة، وهي المناطق التي تسجل أعلى إجهادات ويُحتمل أن تكون عرضة للتلف أو الانهيار بمرور الوقت.
يمكّن هذا التحليل المهندس من اتخاذ قرارات هندسية دقيقة، مثل تعديل الأبعاد، أو تغيير نوع المادة، أو تعزيز نقاط الضعف. وهو جزء أساسي لضمان أن التصميم يلبي معايير السلامة، الكفاءة، والموثوقية قبل المرور إلى مرحلة التصنيع.
The analysis of the main support structure is a critical step in assessing its ability to withstand various operational loads. This analysis is conducted using Finite Element Method (FEM) techniques to simulate the mechanical response of both material and geometry under external forces such as self-weight, equipment loads, and wind pressure.
The simulation is performed using CATIA V5 via the Generative Structural Analysis module. This allows engineers to apply distributed and point loads, define boundary conditions (e.g., fixed supports), and evaluate:
Stress distribution, with a focus on von Mises stress, to determine whether the support risks structural failure under combined loading conditions.
Deformation behavior, to ensure deflections remain within safe limits.
Critical zones, which are high-stress areas that may require reinforcement.
This analysis helps engineers make informed design decisions, such as adjusting dimensions, selecting alternative materials, or reinforcing weak points. It ensures that the structure meets the required standards of safety, durability, and mechanical integrity before proceeding to fabrication.