Effect of the vacuum on Structural and Morphological Properties of Ga2O3 NPs Thin Films by (PLD) Technique
تفاصيل العمل
In this study, thin films of Gallium oxide nanoparticles were equipped using the
method of pulsed laser deposition (PLD)on a glass substrate under different
vacuum conditions (5×10-5, 2×10-2, and 1mbar). The Nd-YAG laser was
utilized at a wavelength of 1064 nm and a frequency of 5 Hz at 130 0C. The
increase effect of the vacuum value on the optical and structural characteristics
was studied by UV-VIS, X-ray diffraction )XRD), scanning electron microscopy
(SEM), and Photoluminescence properties (PL). The outcomes XRD showed that
the structure of Ga2O3 nanoparticles is a polycrystalline structure of the
monoclinic type, with Prominent crystal orientations of (001), (201), (400), (-
202), (111), and (-112). It is according to JCPDS card No.00-041-1103.
Crystallite size for the complete model decreased with the growth of the
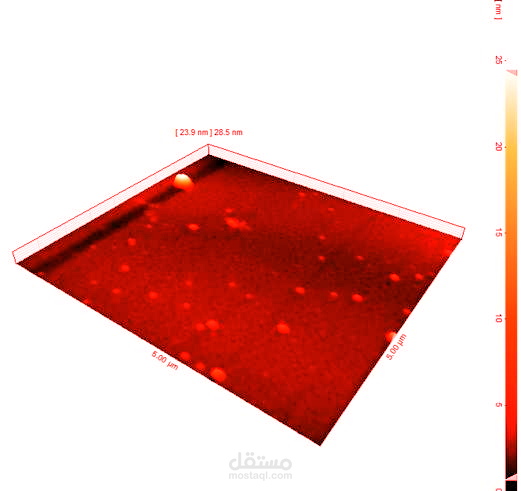
vacuum value. The (SEM) images showed that Ga2o3 nanoparticles are spherical
and homogeneous. The energy band gap increased with increasing the vacuum,
and the absorption upper was in the UV zone. Similar results were obtained from
the researcher MA Yan-Mei et al. [1].