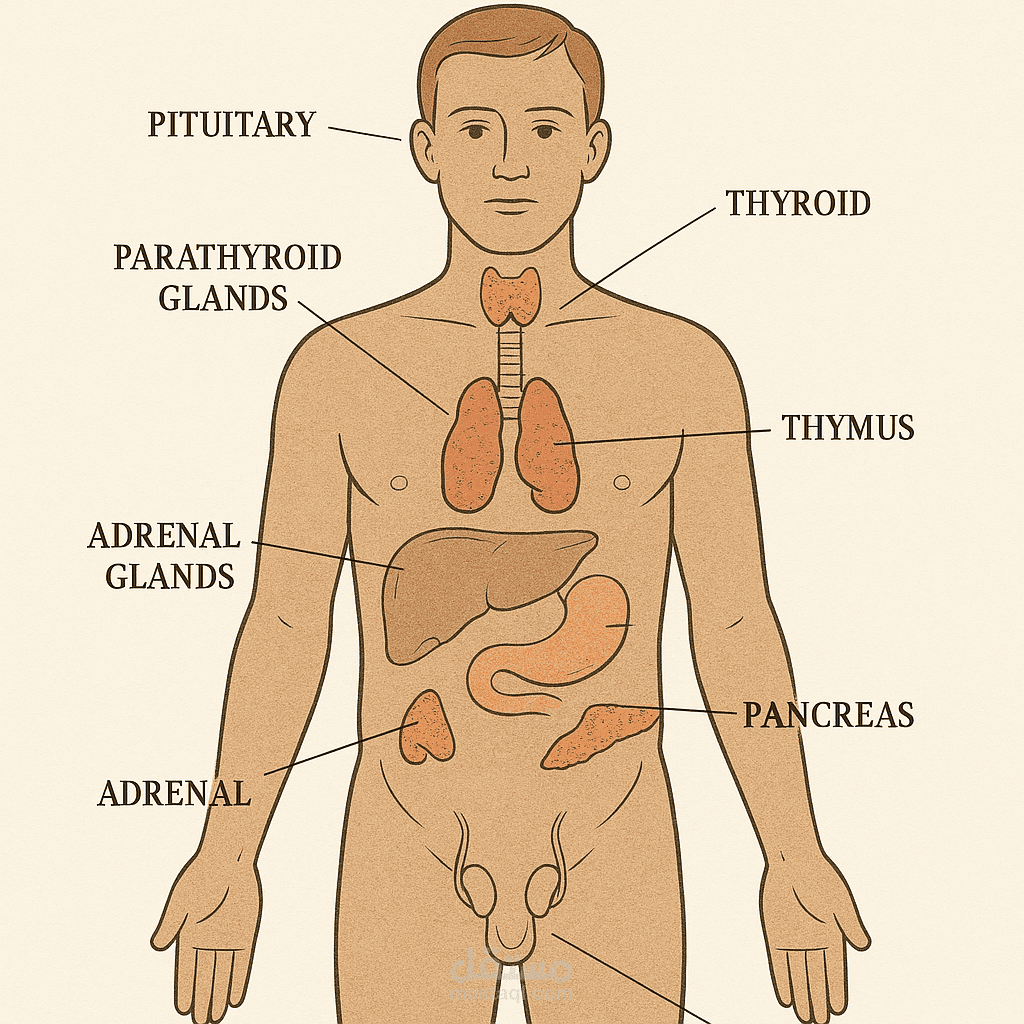
Human body glands
تفاصيل العمل
Here’s an explanation of the major glands in the human body and their functions:
1. Pituitary Gland (Master Gland)
Located at the base of the brain.
Controls other glands and regulates growth, metabolism, and reproductive functions.
Secretes hormones like growth hormone (GH), prolactin, and oxytocin.
2. Hypothalamus
Located above the pituitary gland.
Links the nervous system to the endocrine system by regulating the pituitary gland.
Controls hunger, thirst, body temperature, and sleep cycles.
3. Thyroid Gland
Found in the neck, wrapped around the trachea.
Regulates metabolism and energy levels by producing thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
Produces calcitonin, which helps regulate calcium levels.
4. Parathyroid Glands
Four small glands behind the thyroid.
Regulate calcium levels in the blood, which is essential for muscle function and bone strength.
Produce parathyroid hormone (PTH).
5. Adrenal Glands
Sit on top of the kidneys.
Release adrenaline (for fight-or-flight response) and cortisol (for stress and metabolism regulation).
Also produce aldosterone, which controls blood pressure and salt balance.
6. Pancreas
Located behind the stomach.
Functions as both an endocrine (hormone-producing) and exocrine (digestive enzyme-releasing) gland.
Produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
7. Pineal Gland
Deep in the brain.
Produces melatonin, which controls sleep-wake cycles.
Influences circadian rhythms and seasonal biological changes.
8. Thymus Gland
Located in the upper chest, behind the sternum.
Active during childhood and plays a role in immune system development.
Produces thymosin, which helps in the maturation of T-cells (a type of white blood cell).
9. Ovaries (Female) & Testes (Male)
Ovaries (in females) produce estrogen and progesterone, regulating menstrual cycles and pregnancy.
Testes (in males) produce testosterone, which influences male reproductive development and muscle growth.