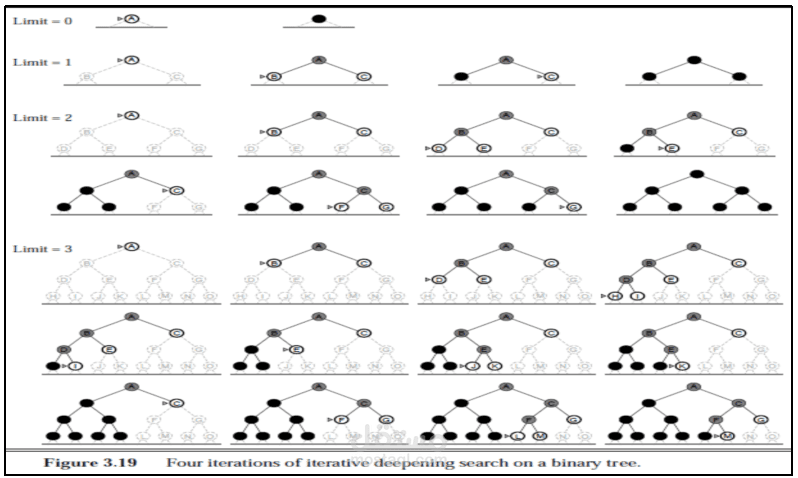
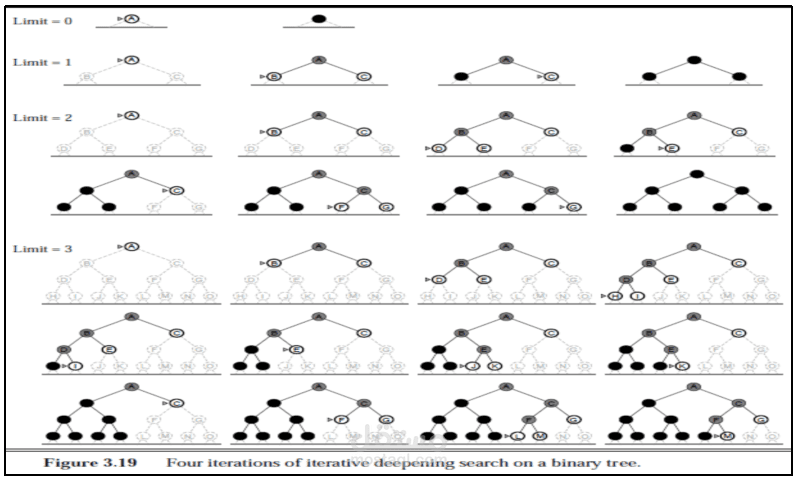
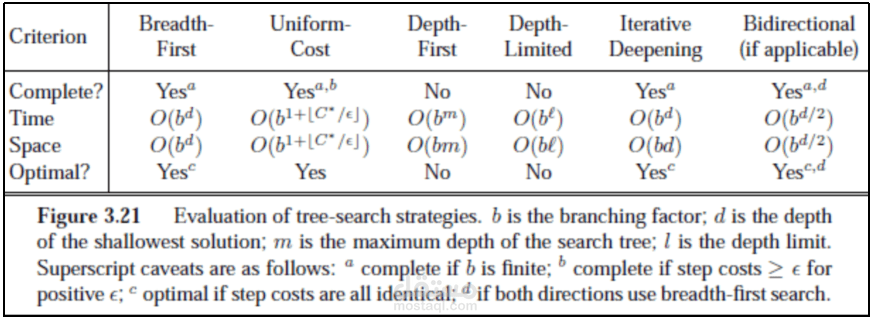
Artificial Intelligence by Omar Waleed
تفاصيل العمل
Artificial Intelligence )AI( attempts replicating the human ways of reasoning
in computing. As a full replication may not be approachable at once due to is magnitude
and complexity, research now targets commercialisable aspects of AI towards providing
“intelligent” assistive services to the human users [1]. Decision making in this paradigm
involves evaluating a number of alternatives in different spatial configurations, environments and circumstances and to find better of the alternatives. It also involves
decision making even when an ideal alternative is not derivable. This paper is therefore
limited to comparing the implementations of the popular AI algorithms, namely Breadth
First Search, Depth First Search, A*, Best First Search and Hill climbing algorithms for
solving a sliding n-puzzle in an attempt to look at the better efficient of the algorithms for
this case. To solve the sliding n puzzle problem, one moves a set of square tiles arranged
randomly in a square board to arrive at a pre-determined order. The board has only one
blank square and each tile can only move to the blank space adjacent to itself. Our aim in
this paper is to apply the AI approaches to the case and compare their performances in the
problem solving
ملفات مرفقة
بطاقة العمل
| اسم المستقل | عمر و. |
| عدد الإعجابات | 0 |
| عدد المشاهدات | 6 |
| تاريخ الإضافة | |
| تاريخ الإنجاز |