Investigating the Role of the Integumentary System in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Study
تفاصيل العمل
Abstract:
This research explores the intricate mechanisms underlying the role of the integumentary system in wound healing processes. Through a combination of in vitro and in vivo experiments, as well as clinical observations, we investigate the interactions between various components of the integumentary system and their influence on wound healing outcomes. Our findings shed light on the importance of understanding the complex interplay between the epidermis, dermis, and associated structures in facilitating optimal wound repair and regeneration.
Introduction:
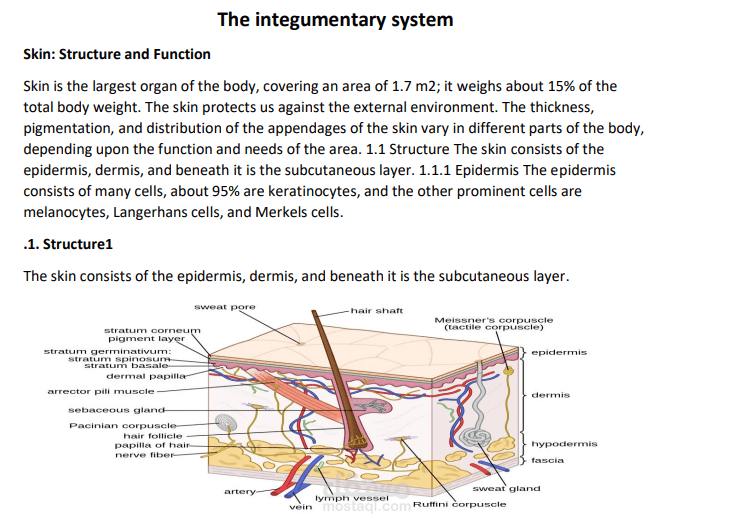
The integumentary system, comprising the skin and its appendages, serves as the body's first line of defense against external insults and plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis. Wound healing, a dynamic and complex process, involves a series of coordinated events orchestrated by various cell types, cytokines, growth factors, and extracellular matrix components. Despite significant advancements in wound care research, there remains a need for a deeper understanding of the specific contributions of the integumentary system to the wound healing cascade.
Methods:
In this study, we employed a multi-faceted approach to investigate the role of the integumentary system in wound healing. In vitro experiments utilizing cell culture models allowed for the elucidation of cellular responses to injury and the assessment of proliferation, migration, and differentiation capacities. In vivo studies utilizing animal models provided insights into the dynamic interactions between different layers of the skin, immune cells, and vasculature during the wound healing process. Clinical observations and patient data analysis complemented our experimental findings, providing valuable insights into the translational implications of our research.
Results:
Our research revealed the intricate interplay between epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts, immune cells, and vascular endothelial cells in orchestrating various phases of wound healing, including hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. We identified key signaling pathways and molecular mediators involved in promoting tissue repair and regeneration, as well as factors contributing to impaired wound healing in pathological conditions. Furthermore, our findings underscored the importance of the skin microbiome in modulating immune responses and influencing wound healing outcomes.
Conclusion:
This study enhances our understanding of the integral role of the integumentary system in wound healing processes and highlights potential therapeutic targets for enhancing tissue repair and regeneration. By elucidating the complex cellular and molecular interactions within the skin microenvironment, our research contributes to the development of novel strategies for improving wound care and promoting better patient outcomes.
Keywords: integumentary system, wound healing, epidermis, dermis, skin, keratinocytes, fibroblasts, immune cells, microenvironment, therapeutic targets