Handwritten Digit Classification with Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
تفاصيل العمل
MNIST Dataset
The MNIST dataset is a well-known benchmark dataset in the field of machine learning and computer vision. It serves as a foundation for various image classification tasks, making it a suitable choice for our project.
Tools and Libraries
To accomplish our goal, we will utilize the following tools and libraries:
TensorFlow: An open-source machine learning framework that provides a foundation for building neural networks.
Keras: A high-level neural networks API that runs on top of TensorFlow, simplifying the model-building process.
Matplotlib: A Python library for creating visualizations and plots.
NumPy: A library for numerical operations in Python.
Data Loading
We begin by importing the necessary libraries and loading the MNIST dataset into our Python environment. The dataset is divided into two sets: training and testing.
Data Analysis
Before constructing our neural network, let's perform some basic analysis of the dataset:
Number of training samples: 60,000
Number of testing samples: 10,000
Image dimensions: 28x28 pixels
Data Preprocessing
To prepare the data for training, we perform the following preprocessing steps:
Data Normalization
We normalize the pixel values of the images to a range between 0 and 1 by dividing each pixel value by 255. This normalization simplifies the training process.
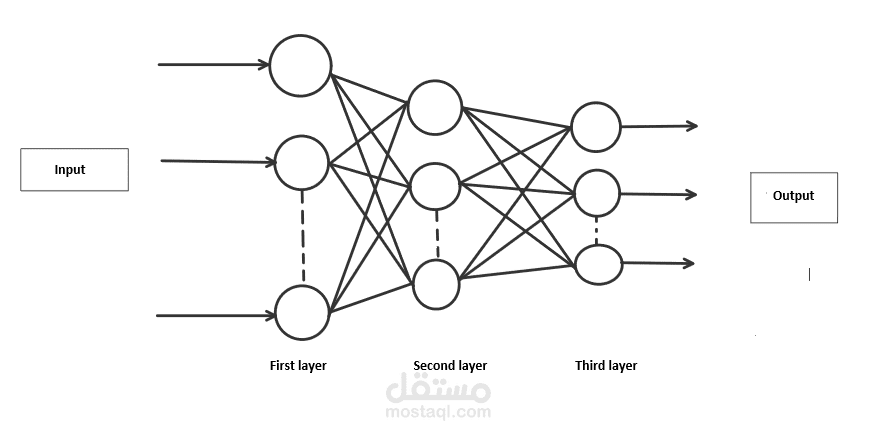
Building the Neural Network Model
The heart of our project is the neural network model. We design it as follows:
Flatten Layer: This layer flattens the 28x28 pixel images into a 1D array with 784 elements.
Hidden Dense Layers: We create two hidden dense layers, each consisting of 128 nodes and employing the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function. These layers help extract relevant features from the data.
Output Dense Layer: The output layer has 10 nodes, each corresponding to a digit from 0 to 9. We use the softmax activation function here, which turns the network's output into probability scores, allowing us to make predictions.
Compiling the Model
Before training, we compile the model. During compilation, we specify the following:
Optimizer: We use the Adam optimizer, a widely used optimization algorithm for training deep neural networks.
Loss Function: The loss function is set to 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy,' which is suitable for multi-class classification problems with integer labels.
Metrics: We track the accuracy metric to evaluate the model's performance during training.
Training the Model
With our model ready, we proceed to train it. We train the model on the training dataset for a specified number of epochs. Each epoch represents one pass through the entire training dataset.
Model Evaluation
Once training is complete, we evaluate the model's performance on the test dataset. We compute the validation loss and accuracy to assess how well the model generalizes to new, unseen data.
Making Predictions
We use our trained model to make predictions on a subset of test images. We display both the test images and the model's predictions, allowing us to visualize how well the model performs.
Model Summary
Finally, we provide a summary of our model's architecture. This summary details the layers, their output shapes, and the total number of trainable parameters in the model.
This project showcases the process of building, training, and evaluating a neural network for handwritten digit classification using the MNIST dataset and TensorFlow/Keras. The ultimate goal is to accurately recognize and classify handwritten digits from 0 to 9.