Network-Intrusion-Detection using Machine Learning
تفاصيل العمل
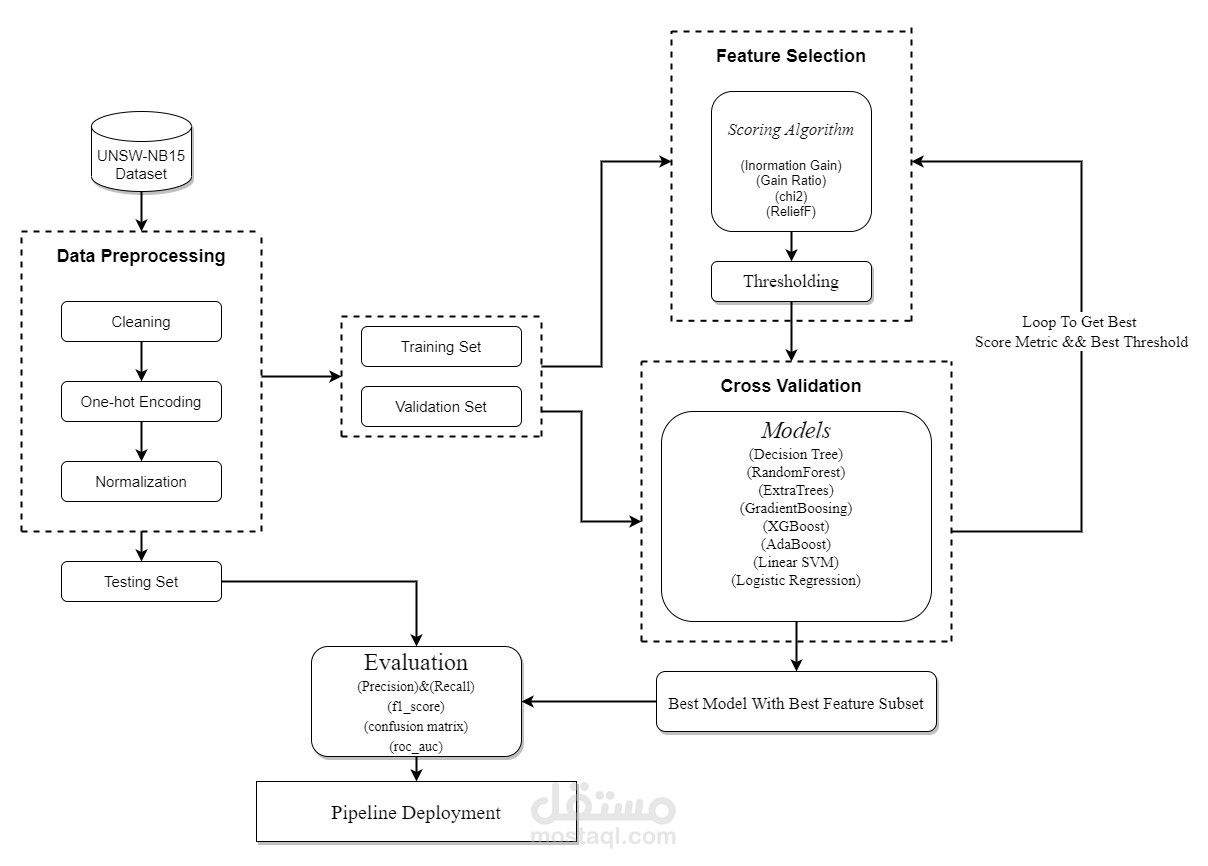
In this work, we explore different datasets for Network Intrusion Detection. The objective is to classify attack signals from normal ones, considering the increasing challenge of computer security and intrusion detection in today's networked environments. Three different datasets were utilized
D1 --> UNSW-NB15 (The primary data)
D2 --> KDDCUP
D3 --> NSL-KDD
Feature Selection Techniques
To build effective models, we utilized various feature selection techniques, namely:
Information gain
Gain ratio
Chi2
Relief
Model Training
We trained different models using ten thresholds and quantized the features from 10% to 90% for each feature selection algorithm. The models we employed include:
Decision trees
Random Forest
Extra trees
Gradient Boosting
XGBoost
AdaBoost
Linear SVM
Logistic Regression
Model Evaluation
To evaluate the performance of the models, we utilized cross-validation on the features selected with different thresholds. The models were compared based on the validation accuracy obtained from cross-validation.
Best Model Resutls
After thorough analysis, we identified 15 features that achieved the highest accuracy of 97.79%. This model was obtained by stacking the best models using the stacking technique.
Conclusion
Through our research, we demonstrated the effectiveness of different feature selection techniques and models in Network Intrusion Detection. By selecting the optimal features and leveraging stacking, we achieved high accuracy in classifying attack signals from normal ones. This work contributes to the advancement of computer security and intrusion detection in networked environments.
Please refer to the corresponding code and documentation for detailed implementation and analysis.