Multi-head Self-attention via Vision Transformer For Zero-shot Learning
تفاصيل العمل
Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) aims to recognise unseen object classes, which are not observed during the
training phase. The existing body of works on ZSL mostly relies on pretrained visual features and lacks
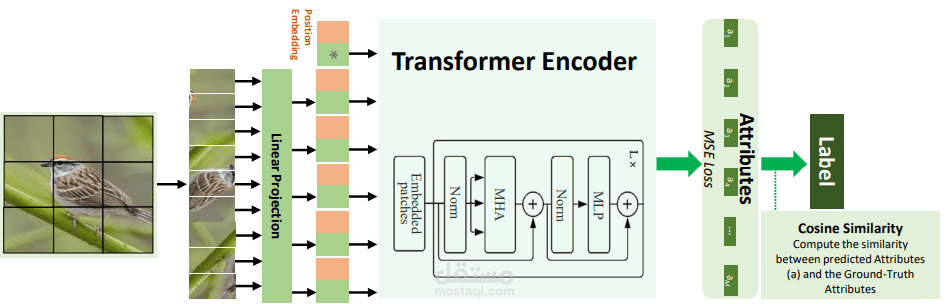
the explicit attribute localisation mechanism on images. In this work, we propose an attention-based model
in the problem settings of ZSL to learn attributes useful for unseen class recognition. Our method uses
an attention mechanism adapted from Vision Transformer to capture and learn discriminative attributes by
splitting images into small patches. We conduct experiments on three popular ZSL benchmarks (i.e., AWA2,
CUB and SUN) and set new state-of-the-art harmonic mean results on all the three datasets, which illustrate
the effectiveness of our proposed method.